IT and Security Roadmap In AI Disruptive Era
In an era where AI is rapidly reshaping business, an IT and security roadmap is more important than ever. It's no longer just about managing technology; it's about strategically leveraging it to gain a competitive edge and ensure your business is resilient. Think of it as a GPS for your organization's digital future, guiding you through the complexities of AI adoption, cybersecurity threats, and the evolving digital landscape.
The Core Purpose of IT Roadmaps
At its heart, an IT roadmap is a strategic blueprint that connects technology initiatives directly to business goals. It's a visual, high-level plan that shows everyone—from the technical team to the C-suite—how IT will enable the company's vision over the short and long term.
A well-crafted roadmap helps you:
- Align Technology with Strategy: It ensures that every IT investment, from a new AI tool to a cloud migration, is a purposeful step toward achieving business objectives like increasing revenue or improving customer experience.
- Optimize Resources: It helps leaders prioritize projects, allocate budgets, and manage personnel efficiently, preventing wasted effort and redundant spending.
- Boost Communication: By presenting complex technical plans in a clear, visual format, it builds consensus and a shared understanding across the entire organization.
How CIOs Can Align IT with Business Strategy
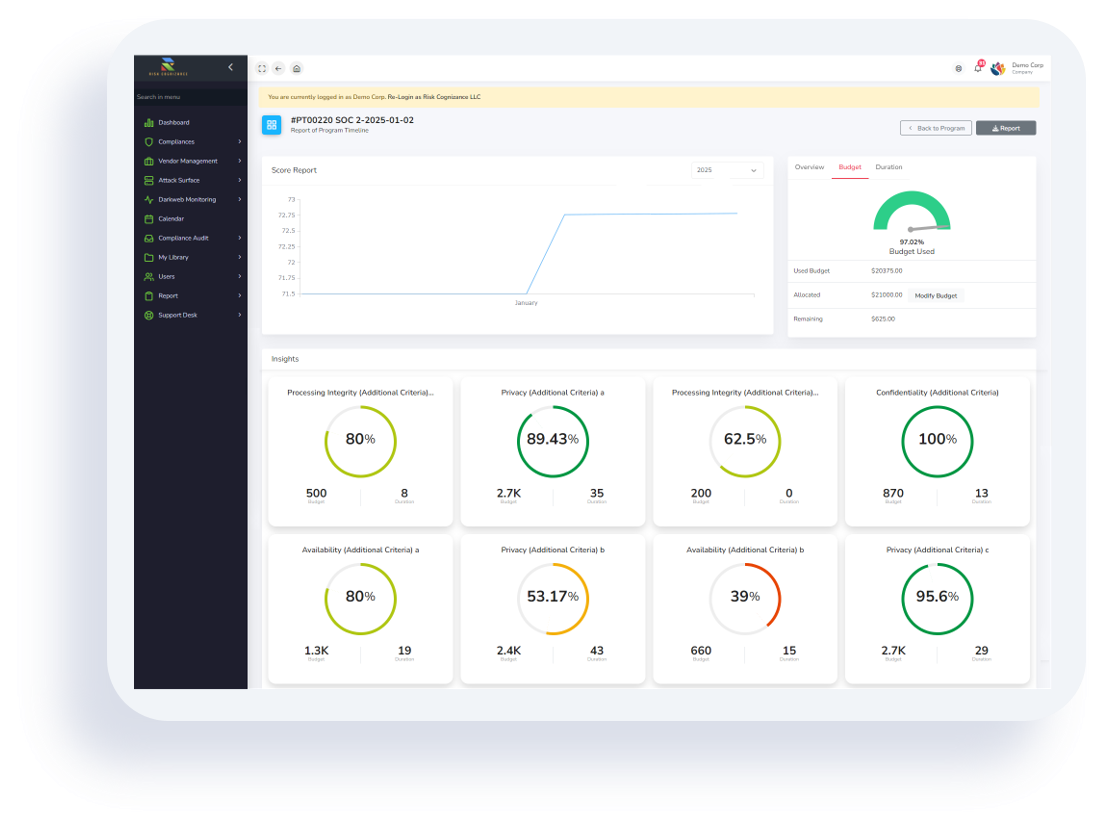
For an IT roadmap to be truly effective, it must be a business roadmap first. CIOs play a crucial role in making this happen by moving IT from a support function to a strategic partner. This alignment is a continuous cycle that involves several key steps:
- Define the Business Drivers: Start by understanding the company's core priorities. What are the major goals for the next year? Is it market expansion, cost reduction, or digital innovation?
- Assess Current IT Capabilities: Evaluate your existing technology and team skills to see what's working and where the gaps are. This provides a clear starting point.
- Identify Opportunities: Pinpoint where technology, especially new advancements like AI, can solve business problems or create new opportunities.
- Set Shared Metrics: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that both business and IT leaders agree on. This ensures everyone's success is measured by the same yardstick—the impact on business outcomes.
- Foster a Collaborative Culture: Alignment isn't a one-time event. It requires an ongoing, two-way dialogue with stakeholders from every department to ensure the roadmap remains flexible and relevant.
Leveraging External Resources to Bridge Capacity Gaps
AI and other disruptive technologies often require specialized skills that are difficult and expensive to hire in-house. This is where external resources become invaluable for addressing internal IT capacity challenges.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs can take over the day-to-day management of your IT infrastructure and security. This frees up your internal team to focus on strategic, value-adding projects.
- Specialized Consultants: For a specific, high-stakes project like an AI implementation, a specialized consultant can provide the deep expertise and strategic guidance you need without the long-term commitment of a full-time hire.
- Staff Augmentation: Need a data scientist for a six-month project? Staff augmentation allows you to temporarily expand your team with highly skilled professionals to accelerate a project and fill a specific skill gap.
Communication and Buy-in: The Human Side of Transformation
The most significant roadblock to digital transformation isn't a lack of technology, but a lack of people-focused communication. Digital transformation is a human process as much as a technological one. Without clear communication and buy-in, even the best-laid plans can fail.
- Reduces Fear and Resistance: Transparent communication addresses employee anxieties about change and job security. When employees understand why the transformation is happening, they're more likely to support it.
- Creates a Shared Purpose: Effective communication turns a technical project into a shared mission. It helps employees see how their role contributes to the bigger picture.
- Ensures Adoption: Buy-in is what drives technology adoption. When employees feel like stakeholders—not just bystanders—they are more likely to use new tools properly and harness their full potential.
What is the fundamental purpose of IT roadmaps?
An IT roadmap is a strategic planning tool that visually outlines short- and long-term technology initiatives within an organization. Its fundamental purpose is to serve as a blueprint for how IT will support and enable broader business objectives. It bridges the gap between technology and business by ensuring that every IT project, investment, and initiative directly contributes to the company's long-term vision, goals, and strategies.
IT roadmaps provide a clear and organized framework for:
- Strategic Alignment: Connecting technology investments directly to business goals, such as increasing revenue, enhancing customer experience, or improving operational efficiency.
- Resource Management: Helping to prioritize initiatives, allocate budgets efficiently, and manage resources like personnel and software to avoid waste.
- Communication & Buy-in: Visually communicating complex technology plans to non-technical stakeholders, fostering consensus and a shared understanding of the path forward.
- Risk Management: Outlining proactive measures for cybersecurity, infrastructure upgrades, and preparing for future disruptions.
How can CIOs align IT roadmaps with business strategy?
Aligning IT roadmaps with business strategy is a continuous process that goes beyond a one-time planning session. CIOs can achieve this alignment by making IT a strategic partner rather than just a support function. The process involves a few key steps:
- Understand Business Drivers: The process must begin with a deep understanding of the company's core business priorities, such as revenue growth, market expansion, or customer retention.
- Audit Current Capabilities: Conduct a thorough assessment of the existing IT infrastructure, applications, and skill sets to understand what is working, what isn't, and where opportunities exist.
- Identify Gaps and Opportunities: Compare the business's strategic needs with the current IT capabilities to identify technology gaps and opportunities, such as implementing AI to automate a process or adopting new cloud systems for scalability.
- Set Shared KPIs: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are jointly defined by both business and IT leaders. This ensures that IT's success is measured by its impact on business outcomes, not just on technical metrics.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Create a continuous feedback loop through regular meetings with stakeholders across departments. This ensures the roadmap remains a living document that can adapt to evolving business needs.
How are external resources addressing internal IT capacity challenges?
External resources are a critical solution for addressing internal IT capacity challenges, especially in a rapidly changing technological landscape. They provide flexibility and specialized expertise that may be difficult or expensive to develop in-house. Organizations leverage these resources in several ways:
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): These third-party companies can take over the management of day-to-day IT operations, such as network management, cybersecurity, and help desk support. This frees up internal IT staff to focus on more strategic, long-term projects.
- Consultants and Contractors: External consultants can be brought in for specific, high-level strategic projects, such as a major cloud migration or an AI implementation, where the company lacks the internal expertise. Contractors can fill short-term staffing gaps for specialized roles or provide flexible labor for project-based work.
- Staff Augmentation: Companies can use external resources to supplement their existing teams with specific skills, such as a data scientist or a security analyst, to accelerate projects and overcome skill shortages without the long-term commitment of a full-time hire.
Why is communication and buy-in critical for digital transformation?
Communication and buy-in are arguably the most critical factors for a successful digital transformation. Without them, even the most innovative technology initiatives are likely to fail. This is because digital transformation is not just a technological challenge; it is a human challenge.
- Builds Trust and Reduces Resistance: Clear, consistent, and transparent communication helps to demystify the transformation process. It addresses employees' fears and skepticism about job security and change, building trust and reducing resistance.
- Creates a Shared Purpose: When employees understand the "why" behind the changes—how a new system will improve their work, help the company, or enhance the customer experience—they are more likely to embrace the initiative and become active participants.
- Promotes Engagement: Communication should be a two-way dialogue, not a one-way announcement. By seeking employee feedback and involving them in the planning process, leaders can turn employees from passive bystanders into active stakeholders.
- Ensures Adoption: Effective communication and strong buy-in are what lead to the proper adoption and full utilization of new technologies. Without it, new systems may go unused, resulting in wasted investment and missed opportunities.
The Importance of Intentional Communication
While specific details on Jenica McHugh's personal methodology are not widely available, her work often emphasizes the concept of intentional communication. This suggests that an effective IT roadmap isn't just a document—it's a communication tool. The key is to tailor your message to different audiences. What's important to an engineer is different from what an executive needs to know. By communicating with intention, you ensure everyone understands the vision and their role in making it a reality.


