How AI is Changing the GRC Strategy
How AI is Changing the GRC Strategy
Compliance IT Governance Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the modern business landscape and reshaping how organizations govern data, manage compliance, and assess risk. For today’s CISOs, risk officers, and compliance leaders, the challenge is not simply adopting AI, but ensuring that AI-driven operations remain secure, ethical, and compliant.
As AI becomes central to decision-making, automation, and cybersecurity, the integration of AI-powered Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) frameworks has become essential to maintain trust, transparency, and regulatory adherence.
The Rise of Intelligent GRC: A Strategic Imperative
Traditional GRC frameworks were designed for structured processes, focused on policy management, compliance tracking, and audit readiness. However, as enterprises adopt AI, cloud infrastructure, and data-driven automation, these frameworks must evolve to address dynamic and adaptive risks that shift in real time.
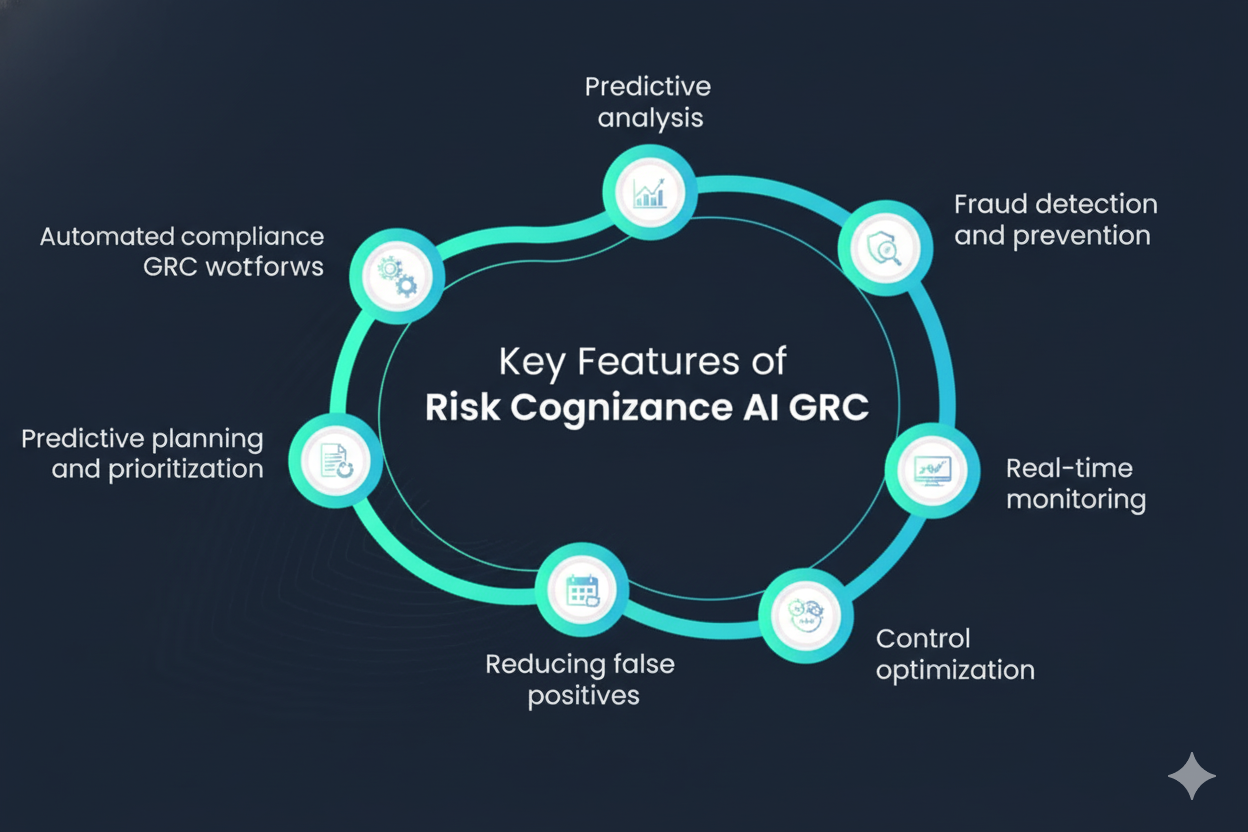
AI-driven GRC platforms, such as those developed by Risk Cognizance, offer a smarter approach. These tools continuously monitor compliance controls, detect anomalies, predict threats, and automate audit workflows. By combining data analytics with governance automation, organizations gain visibility and control over compliance programs that once required extensive manual effort.
Key benefits of intelligent GRC systems include:
- Continuous compliance with frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, SOC 2, GDPR, and CMMC.
- Automated risk identification through AI-based anomaly detection.
- Unified governance workflows for IT, cybersecurity, and enterprise operations.
- Predictive risk intelligence that reduces exposure before incidents occur.
As AI expands, GRC must not only monitor how organizations use it but also how AI itself influences business risk and compliance posture.

AI Governance: Building a Trustworthy Framework
AI introduces a new dimension of governance challenges — including transparency, data ethics, bias, and shadow AI. To manage this, organizations are embedding AI Governance into their broader GRC structures.
A modern AI GRC framework includes:
- Governance: Clear accountability for AI decisions, usage policies, and ethical oversight.
- Risk Management: Identification and evaluation of risks like data leakage, bias, hallucinations, and algorithmic errors.
- Compliance: Integration with industry frameworks such as NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001, and COSO to ensure AI use aligns with global regulatory standards.
- Assurance and Monitoring: Continuous tracking of AI systems to ensure outputs remain trustworthy, explainable, and compliant.
These frameworks provide clarity not only for regulators but also for insurers evaluating an organization’s risk maturity.
Understanding Technology Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O) and Cyber Insurance
As AI and automation become embedded in everyday business operations, insurance coverage plays a crucial role in protecting organizations from financial and reputational loss. Two core policies dominate this space: Technology Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O) and Cyber Insurance.
While they are often mentioned together, they cover very different risk vectors — and understanding their differences is vital for holistic protection.

What Is Technology Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O) Insurance?
Tech E&O insurance protects businesses that develop or deliver technology products and services against claims of professional negligence, product failure, or non-performance.
This coverage is critical for organizations that rely on software, data analytics, or AI models to deliver client outcomes. If a product or algorithm fails — causing financial harm or operational disruption — Tech E&O helps cover:
- Legal defense and settlements due to product or service failure.
- Claims arising from faulty AI recommendations, model drift, or integration errors.
- Losses caused by software bugs, downtime, or performance issues.
For example, an AI system that provides inaccurate financial forecasting or a GRC automation tool that fails to detect compliance gaps could expose a business to liability claims. Tech E&O ensures that such incidents do not result in catastrophic financial loss.
- Tech E&O is especially vital for:
- AI and data analytics vendors.
- SaaS and cloud solution providers.
- Cybersecurity consultants and managed service providers.
- RegTech, FinTech, and GovTech platforms.
What Is Cyber Insurance?
Cyber Insurance provides financial protection from cyberattacks, data breaches, ransomware incidents, and privacy violations. It covers the costs associated with both recovery and legal obligations after a digital incident.
Typical coverage includes:
- Data breach response: Legal guidance, customer notification, and credit monitoring.
- Forensic investigation: Root cause analysis and digital forensics to determine breach impact.
- Ransomware and extortion payments: Including negotiation and restoration.
- Business interruption losses: Covering downtime caused by cyber incidents.
- Third-party liability: If personal or client data is compromised.
Cyber Insurance focuses on external threats, while Tech E&O covers internal operational errors. Together, they form a complete safety net for technology-driven enterprises.
Tech E&O vs. Cyber Insurance: The Key Differences
| Coverage Area | Technology Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O) | Cyber Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Professional liability, software or system failure | Cyberattacks, data breaches, ransomware |
| Trigger Event | Client loss due to product or service failure | Unauthorized access or malicious attack |
| Primary Protection | Legal defense, settlements, negligence claims | Breach response, restoration, ransom recovery |
| Beneficiaries | Tech providers, SaaS, consultants | Any business storing or processing data |
| Example Scenario | AI model fails, causing client losses | Ransomware attack halts operations |
While both are critical, neither alone provides full protection for organizations need both E&O and Cyber coverage for complete resilience.
Why Knowing the Difference Matters
Understanding the distinction between E&O and Cyber Insurance allows compliance and risk teams to create comprehensive coverage strategies that align with organizational risk appetite.
- Without E&O, a company may face liability for AI errors or service failure. Without Cyber coverage, it remains exposed to external cyber incidents.
- For organizations integrating AI, both policies are essential to manage evolving risks in the digital economy.
- This distinction also influences how insurers evaluate premium rates and coverage conditions.
Organizations with strong GRC maturity, supported by automated monitoring, incident response, and data governance, can often negotiate lower premiums.
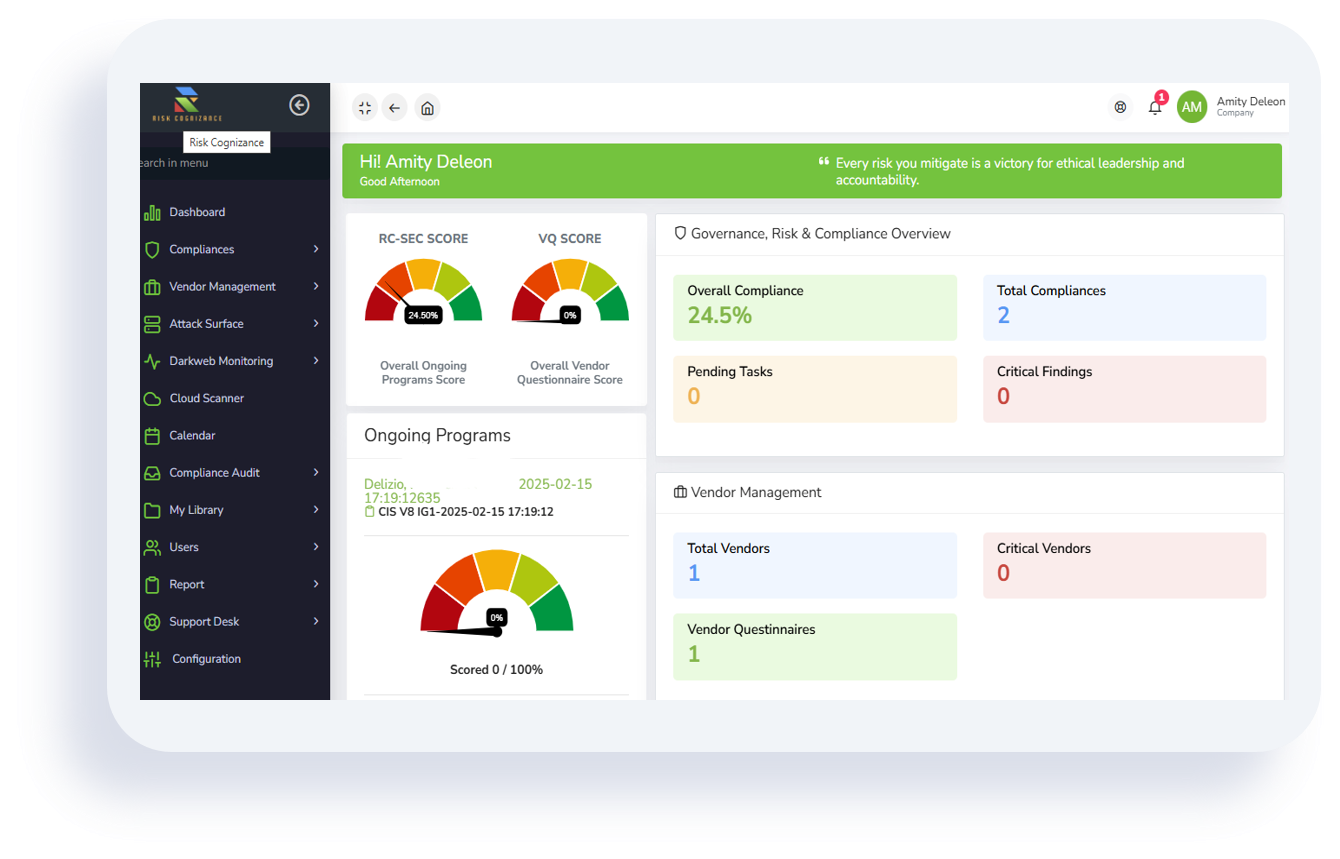
How AI-Powered GRC Platforms Reduce Insurance Costs
AI-enhanced GRC platforms like Risk Cognizance are changing the way businesses manage compliance and insurance exposure. By integrating real-time risk visibility, automated evidence collection, and incident detection, organizations demonstrate operational maturity and regulatory readiness — key factors insurers assess when underwriting policies.
Key ways AI GRC reduces premiums:
- Automated risk control validation shows proactive defense mechanisms.
- Continuous compliance reports help insurers verify control effectiveness.
- Predictive analytics identify and prevent high-impact risks early.
- Integrated audit trails provide verifiable documentation for claims defense.
This proactive approach not only strengthens resilience but also builds credibility with insurers, partners, and regulators.
Adapting GRC Frameworks to Address AI Risks
To stay ahead of regulatory and insurance demands, organizations are adapting existing GRC frameworks — such as ISO 27001, NIST 800-53, COSO, and COBIT — to include AI-specific controls like data lineage, model validation, and bias monitoring.
Core Pillars of AI GRC Integration
Enterprise Risk Management: Defines AI risk appetite and integrates model governance committees.
- Model Risk Management: Ensures accuracy, fairness, and resilience of AI models.
- Operational Governance: Embeds human oversight and continuous validation mechanisms.
- IT Risk and Compliance: Aligns AI deployment with data protection and security standards.
These pillars enable organizations to scale innovation without compromising compliance or safety.
The Future of AI-Driven GRC and Insurance Alignment
As AI becomes both a tool for innovation and a source of new risks, the future of GRC lies in collaboration between cybersecurity, compliance, and insurance ecosystems.
Organizations that embed AI GRC tools early will not only enhance operational resilience but will also gain competitive advantages such as:
- Faster regulatory approval and audit readiness.
- Lower total cost of compliance.
- Greater insurer trust and reduced liability exposure.
- Enhanced business continuity through predictive insights.
Conclusion
AI is redefining how organizations perceive and manage risk. The convergence of AI governance, GRC automation, and insurance integration provides a powerful framework for long-term resilience.
By understanding the distinctions between Technology Errors & Omissions and Cyber Insurance, and implementing AI-powered GRC solutions, businesses can mitigate risk, reduce insurance costs, and ensure trust in their digital ecosystem.
Risk Cognizance’s intelligent GRC platform enables enterprises to unify compliance, governance, and cybersecurity into one adaptive ecosystem — empowering leaders to innovate safely while maintaining regulatory confidence.