
184 Million Users’ Passwords Exposed From an Open Directory Controlled by Hackers
Proactive Data Breach Prevention: Attack Surface Management & GRC Tools
A cybersecurity researcher recently discovered a massive, unprotected online database containing over 184 million unique login credentials, including usernames and passwords for a vast array of services. This massive trove of data, totaling over 47 gigabytes, was found in an open directory, meaning it was not encrypted or password-protected, leaving it openly accessible to anyone who knew where to look.
The exposed data includes credentials for highly sensitive platforms such as:
- Major tech giants: Apple, Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Instagram, Discord, Snapchat, Spotify, WordPress, Yahoo, and Amazon.
- Financial institutions: Bank and financial accounts.
- Healthcare platforms.
- Government portals: Including .Gov credentials from countries like Australia, Iran, India, Romania, and Brazil.
The security researcher, Jeremiah Fowler, described this as "one of the most dangerous discoveries I have found in a very long time" due to the sheer scale and diversity of the compromised accounts. The data appeared to be harvested by "infostealer malware," a type of malicious software designed to pilfer sensitive information from various platforms.
After being notified, the hosting provider quickly took the database offline, but it's unknown how long it was publicly accessible or how many malicious actors may have accessed it.
Leveraging Risk Cognizance for Breach Prevention and Response:
This incident underscores the critical need for both proactive data breach prevention and robust post-breach response capabilities. Risk Cognizance offers integrated solutions to address both aspects:
For Proactive Prevention: Utilizing Risk Cognizance's Attack Surface Management (ASM) and GRC Platform
To effectively prevent breaches like this, organizations need a proactive and continuous understanding of their digital footprint, coupled with strong governance and compliance controls.
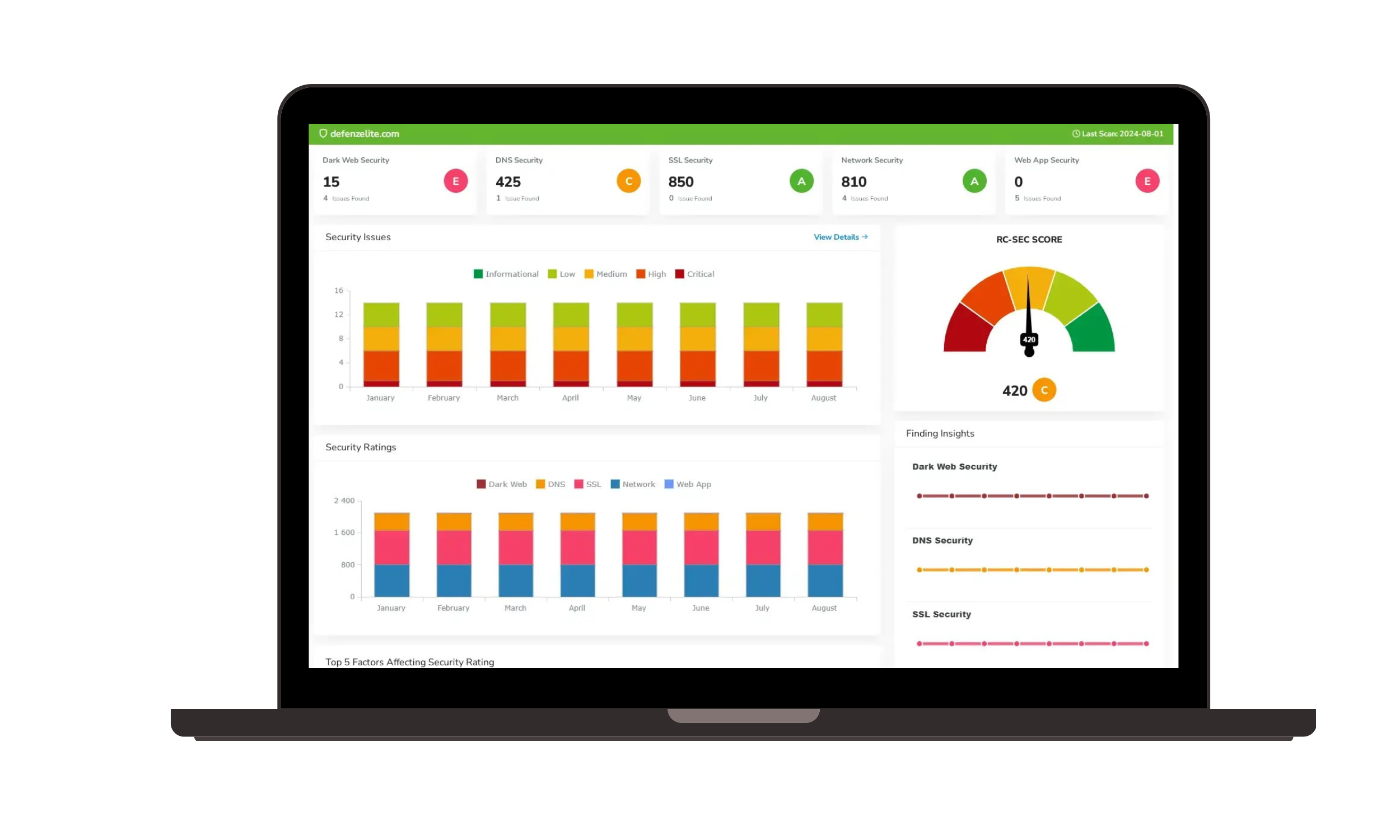
- Risk Cognizance's Attack Surface Management (ASM) Tools: This solution is designed for continuous discovery and assessment of your digital assets. It helps you:
- Continuously Discover and Map Assets: ASM automatically identifies all your internet-facing assets, including those that might be unknown ("shadow IT"), misconfigured cloud resources, or vulnerable third-party connections. This is crucial because you can't protect what you don't know exists.
- Identify and Prioritize Vulnerabilities: The platform continuously scans these assets for weaknesses, misconfigurations, and potential attack vectors. It then prioritizes these vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact, allowing your team to focus on the most critical risks first.
- Reduce Exposure: By highlighting and categorizing risks in real-time, Risk Cognizance ASM helps you proactively address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by cybercriminals, effectively shrinking your attack surface.
- Risk Cognizance's GRC Platform: A robust GRC platform underpins effective breach prevention by ensuring a strong security posture from the ground up:
- Policy & Procedure Management: Ensures that up-to-date security policies and procedures are in place, communicated, and adhered to across the organization, forming the foundational layer of your defense.
- Compliance Management: Helps organizations continuously meet regulatory requirements and industry standards related to data protection (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA), reducing the likelihood of vulnerabilities that could lead to breaches.
- Risk Management: Enables systematic identification, assessment, and mitigation of information security risks, ensuring that potential breach points are identified and addressed proactively through integrated risk registers and dashboards.
For Rapid Detection and Comprehensive Response: Utilizing Risk Cognizance's Dark Web Monitoring & Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)
Even with the most robust prevention, breaches can occur. When they do, rapid detection, understanding the full impact, and effective response are paramount.
- Risk Cognizance's Dark Web Monitoring Cyber Intelligence Platform: This crucial tool continuously scans dark web forums, marketplaces, and hidden services for leaked credentials, sensitive data, and other compromised information related to your organization, executives, and employees. Proactive alerts from this service can inform you immediately if your data, or data of your employees, appears in breaches like the one described, allowing for swift action such as forced password resets or account lockouts.
- Risk Cognizance's Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) Software: Breaches often originate through vulnerabilities in the supply chain or via compromised third parties. TPRM helps you:
- Assess Vendor Security: Systematically evaluate the security posture of your vendors and partners to understand their potential to introduce risk to your organization.
- Monitor Third-Party Exposure: Continuously monitor the security and compliance status of your extended ecosystem, identifying if any of your third parties have been compromised, which could indirectly impact your data. This is crucial for understanding the full scope and potential ripple effects of a breach.
- Manage Vendor Due Diligence: Ensure that all third parties handling your sensitive data meet your security and compliance requirements, significantly reducing the likelihood of a breach originating from their environment.
This incident underscores the critical importance of a multi-layered security approach. By leveraging Risk Cognizance's Attack Surface Management and its overarching GRC Platform for proactive prevention, and its Dark Web Monitoring and Third-Party Risk Management for rapid detection and comprehensive response, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against devastating data breaches and fortify their overall security posture.
A Summary of Recent Data Breaches (2023-2025)
The past few years have seen an relentless surge in data breaches, highlighting the escalating challenges organizations face in protecting sensitive information. These incidents vary in scale and impact, but collectively underscore the persistent threat landscape driven by sophisticated cybercriminals and common vulnerabilities.
2025 (Early Trends & Notable Incidents):
While the year is still young, 2025 has already seen significant data breaches, with healthcare continuing to be a prime target due to the sensitive nature of patient data. Incidents like the Yale New Haven Health System breach (affecting over 5.5 million patients) and the VeriSource Services breach (impacting 4 million individuals, primarily employees and dependents) illustrate the ongoing vulnerability. Supply chain attacks remain prevalent, with organizations like Hertz Corporation and WK Kellogg Co being impacted by breaches originating from third-party file transfer platforms, even affecting critical infrastructure entities like PJM Interconnection. Misconfigurations and compromised credentials continue to be significant entry points, as seen in the Oracle Cloud breach and the TeleMessage breach affecting US government officials' private communications.
2024 (Major Impacts & Cloud Vulnerabilities):
2024 was marked by several colossal breaches, some with staggering numbers of affected individuals:
- National Public Data Breach: One of the largest, potentially compromising personal information for billions of individuals, highlighting the risks associated with data brokers and broad data collection.
- Ticketmaster Data Breach: Impacting over 560 million customers globally, exposing personal and financial information.
- AT&T Data Breach: Affected approximately 73 million current and former customers, exposing sensitive data including Social Security numbers.
- Snowflake Cloud Data Breaches: A series of incidents where over 165 customer environments on the Snowflake cloud data platform were compromised, impacting major corporations like Ticketmaster and Santander Bank, often due to compromised customer credentials lacking MFA.
- Change Healthcare Ransomware Attack: A devastating incident in the healthcare sector, causing widespread disruption and impacting millions of patient records due to a ransomware attack that highlighted vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
- UK Ministry of Defence Data Breach: A significant breach of a contractor-operated payroll system, exposing data of military personnel, underlining supply chain risks in national security contexts.
2023 (Ransomware Dominance & Supply Chain Exploits):
2023 saw a continued dominance of ransomware and the widespread exploitation of supply chain vulnerabilities:
- MOVEit File Transfer Tool Breach: This was one of the most impactful supply chain attacks, with a zero-day vulnerability in the popular file transfer software exploited by the Clop ransomware group, affecting hundreds of organizations globally, including government agencies, financial institutions, and healthcare providers.
- T-Mobile Data Breaches: T-Mobile continued to experience breaches, with incidents affecting millions of customers through API exploitation and network vulnerabilities.
- MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment Breaches: Major casino and hotel chains were hit by ransomware attacks, causing significant financial losses and operational disruptions.
- 23andMe Data Breach: A credential stuffing attack compromised millions of user accounts, leading to the exposure of genetic and personal data.
- DarkBeam Data Leak: Over 3.8 billion records were exposed due to a misconfigured Elasticsearch database, an example of basic misconfigurations leading to massive data exposure.
- ChatGPT Data Breach: A bug in an open-source library exposed user billing information and chat history, raising concerns about security in emerging AI technologies.

These summaries highlight recurring themes: the critical importance of strong access controls, the pervasive threat of ransomware, the increasing focus on supply chain and third-party risk, and the dire consequences of misconfigurations and unpatched vulnerabilities. Proactive, integrated security measures are no longer just good practice, but an absolute necessity.

.jpg)
