Overview
We explore key areas of risk management for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and provide actionable steps to establish a robust framework and integrate it into your operations.
What is Risk Management for MSPs and MSSPs?
Risk management for MSPs involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats that could impact service delivery, client relationships, or business continuity. Proactive risk management helps MSPs build trust, ensure compliance, and maintain operational efficiency.
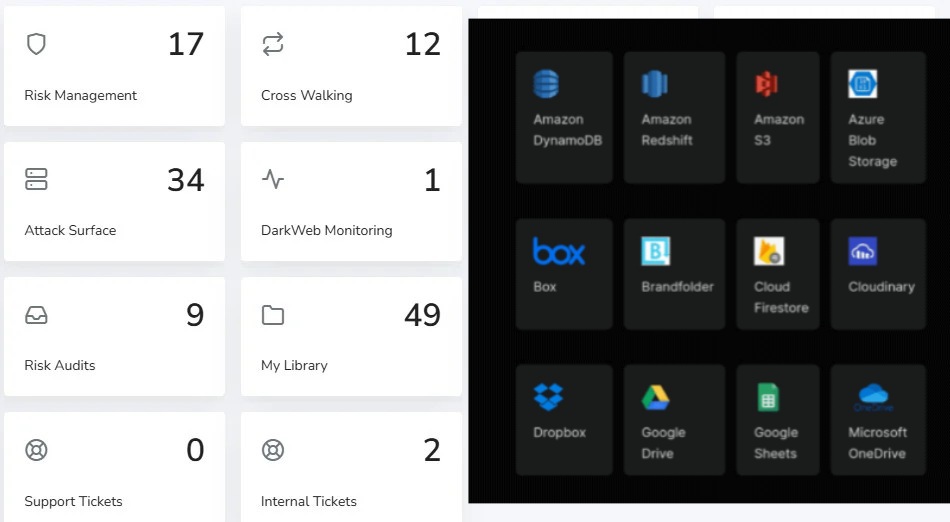
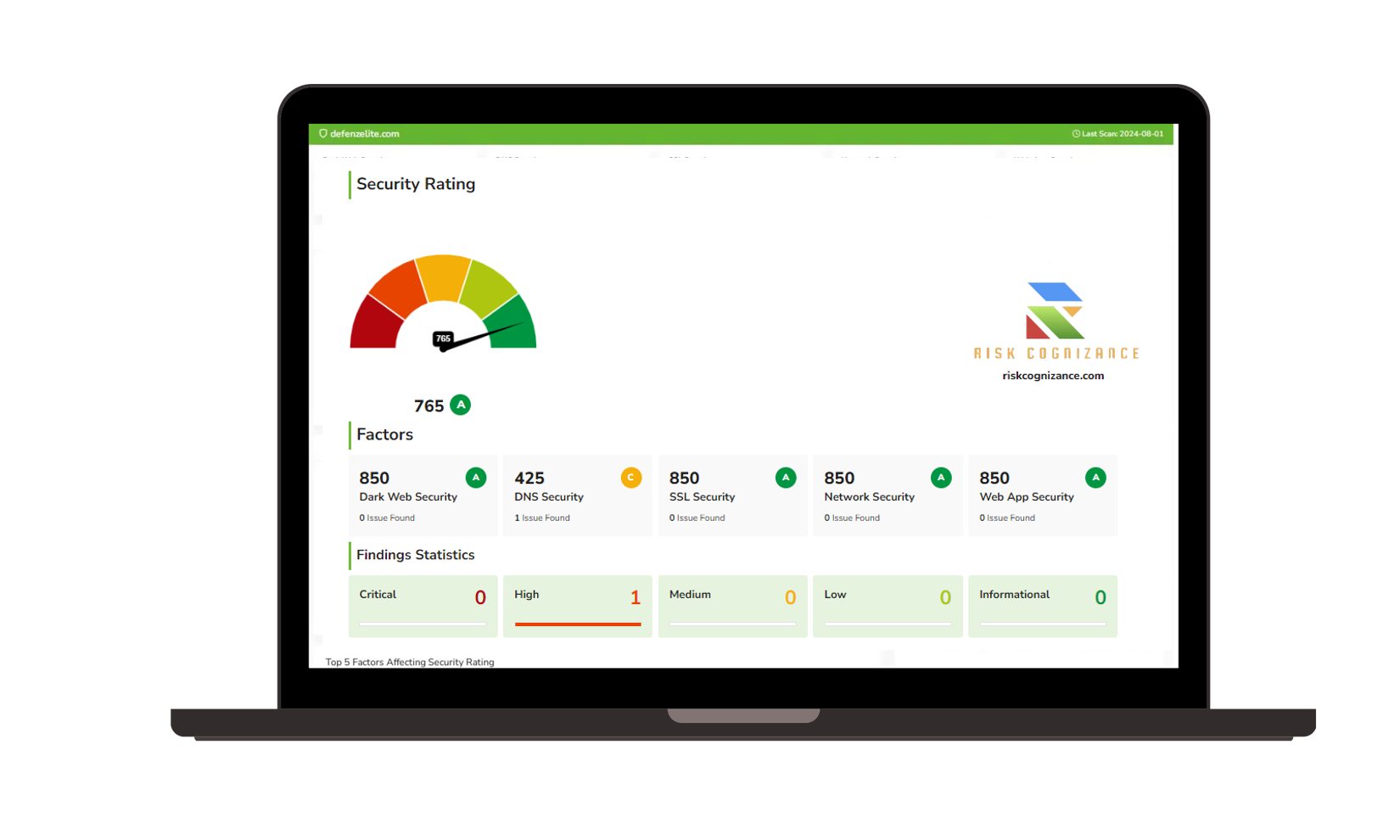
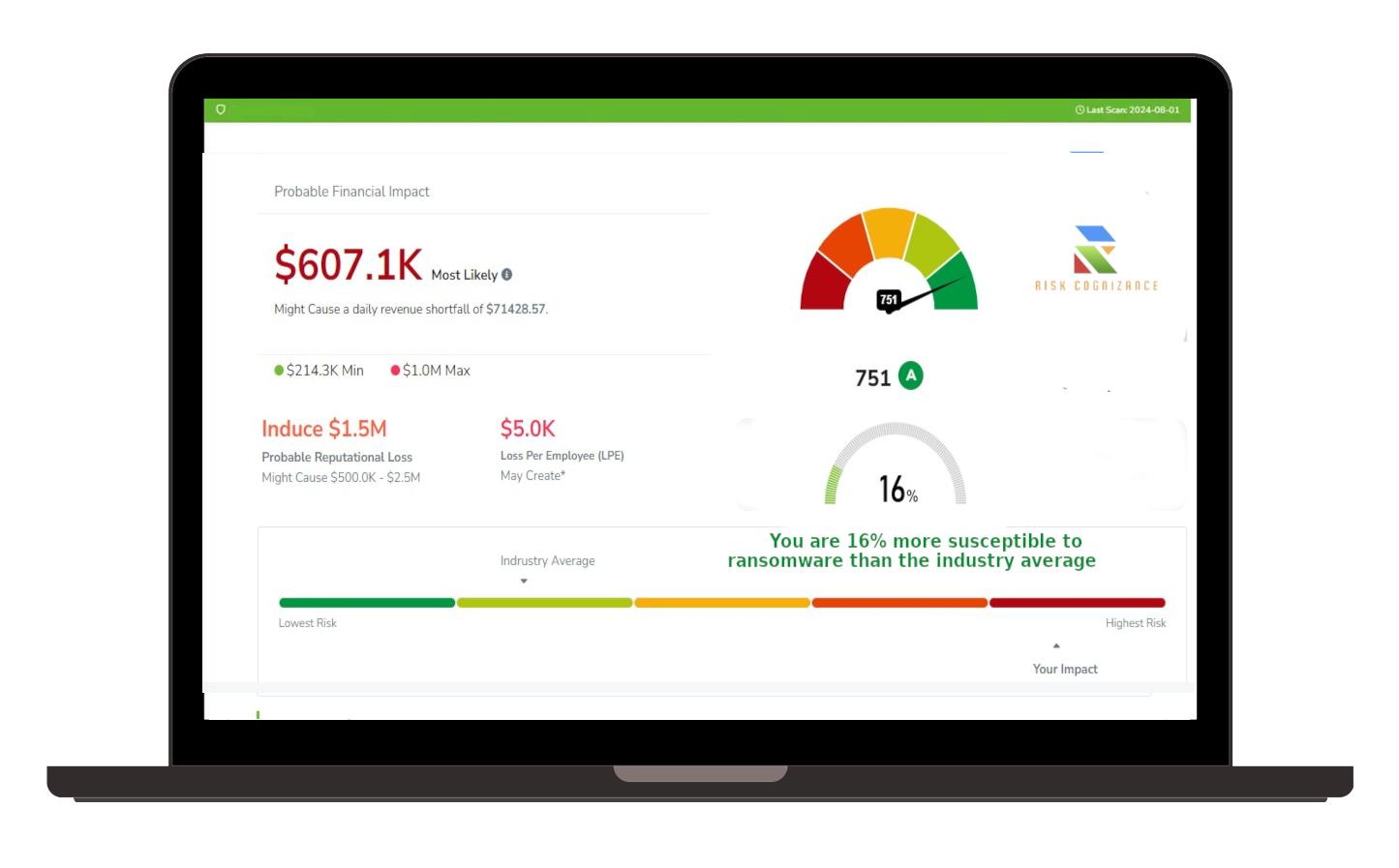
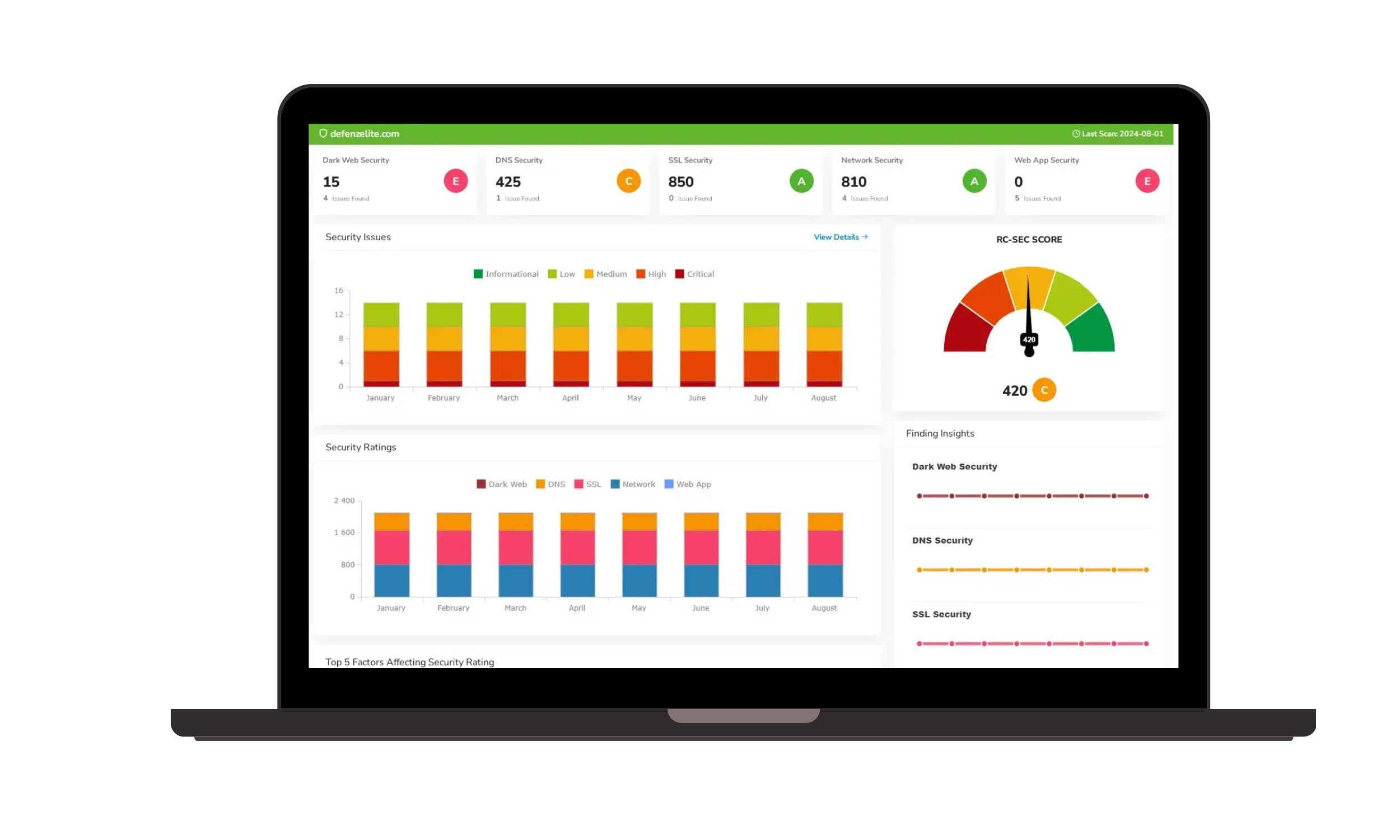
Risk Rating Scorecard
The Risk Rating Scorecard provides organizations with a clear, concise, and data-driven assessment of their overall cybersecurity risk exposure. This risk rating analysis scorecard combines key security metrics into a single risk score, offering clarity and direction for strategic planning. Key benefits include:
- Comprehensive Risk Evaluation: Combines key cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities into a single, easy-to-understand risk score.
- Prioritized Threat Intelligence: Identifies the most critical security risks for focused attention and remediation.
- Strategic & Data-Driven Insights: Empowers decision-makers with actionable intelligence to strengthen cybersecurity strategies.
- Industry Benchmarking: Compare your risk rating to industry peers to understand your security standing.
The Risk Rating Scorecard provides organizations with a clear, strategic overview of their cybersecurity risks, enabling improved threat management, compliance, strategic planning, and enhanced defense mechanisms.
 |  |
 |  |
| |
Key Areas of MSP Risk Management
1. Cybersecurity Risks
MSPs often manage sensitive client data, making cybersecurity a top priority.
- Threat Identification: Detect vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
- Incident Response: Develop and test incident response plans to mitigate attacks.
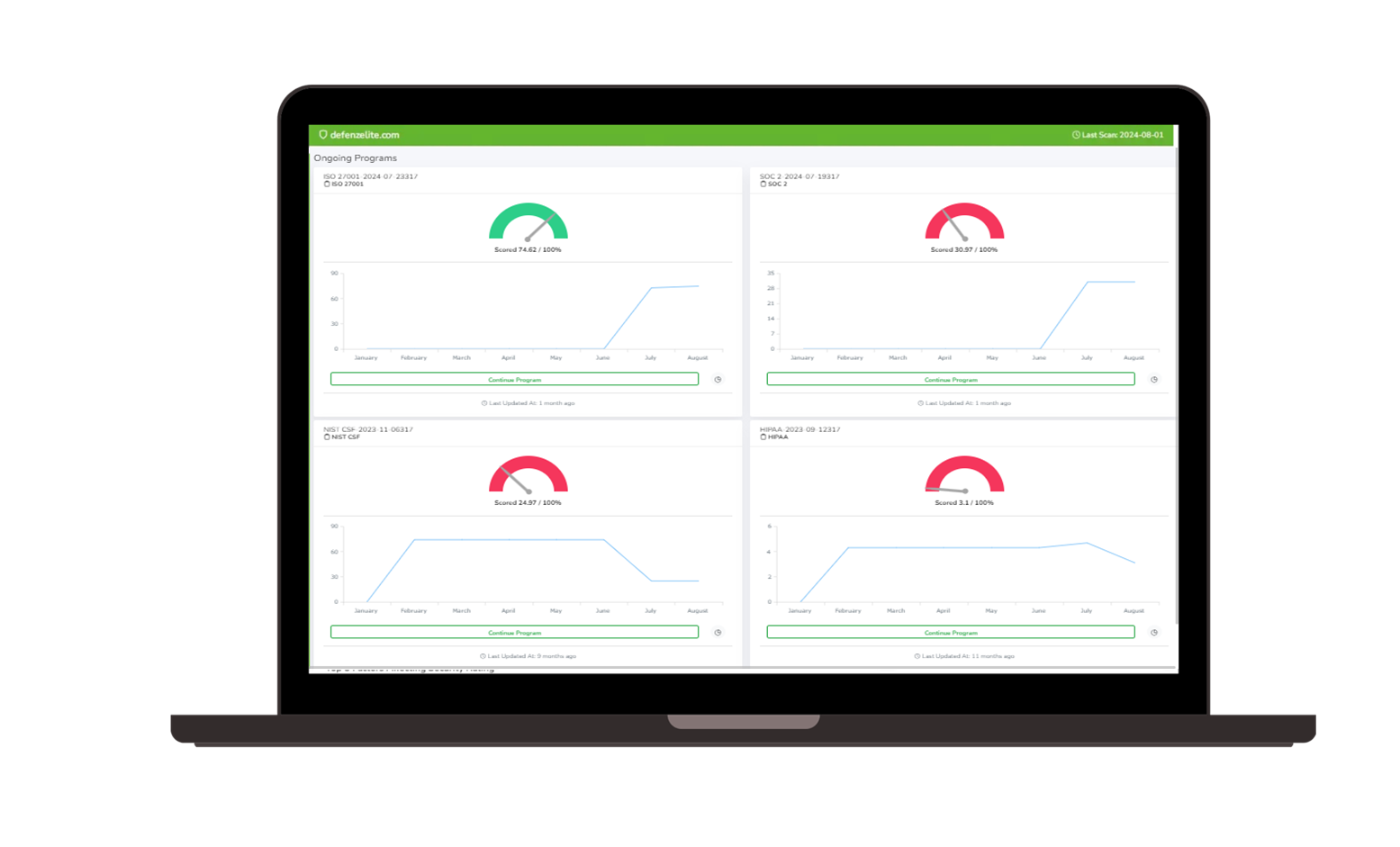
- Compliance: Align with frameworks like NIST CSF, SOC 2, and ISO 27001 to ensure regulatory adherence.
2. Data Protection and Privacy
Ensuring the safety and integrity of client data is critical.
- Backup and Recovery Plans: Implement robust data backup strategies to avoid data loss.
- Encryption: Use end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- Privacy Compliance: Meet GDPR, HIPAA, and other privacy regulations relevant to your clients.
3. Financial Risks
Prevent revenue loss and financial instability through effective planning.
- Contractual Clarity: Clearly define service levels, penalties, and terms in client agreements.
- Budget Management: Maintain sufficient reserves for unexpected operational costs.
- Fraud Prevention: Regularly audit transactions and accounts for suspicious activity.
4. Vendor and Supply Chain Risks
MSPs rely on third-party vendors for software, hardware, and services.
- Vendor Assessment: Evaluate the cybersecurity posture of your vendors.
- Dependency Management: Avoid reliance on a single vendor to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously assess vendor performance and compliance.
5. Operational Risks
Operational risks can disrupt service delivery and client satisfaction.
- Business Continuity Plans (BCP): Ensure service availability during disruptions.
- Process Optimization: Streamline internal workflows to reduce inefficiencies.
- Staff Training: Educate employees on best practices for risk prevention and incident handling.
6. Legal and Compliance Risks
Non-compliance with regulations can result in fines and reputational damage.
- Regular Audits: Conduct internal audits to ensure adherence to laws and frameworks.
- Policy Updates: Keep policies and procedures updated with the latest regulatory changes.
- Legal Consultation: Work with legal experts to draft contracts and policies.
Steps to Build a Risk Management Framework for MSPs and MSSPs
Step 1: Define Risk Categories
Identify all potential risks, including cybersecurity, financial, operational, and legal risks.
Step 2: Risk Assessment
Evaluate the likelihood and impact of identified risks to prioritize them effectively.
Step 3: Develop Mitigation Strategies
Create actionable plans to reduce or eliminate risks, including security controls, insurance, and compliance measures.
Step 4: Implement Monitoring Tools
Utilize software tools to continuously monitor risk factors, such as SIEM systems, vulnerability scanners, and compliance platforms.
Step 5: Train Employees
Educate your team on the importance of risk management and their roles in mitigating risks.
Step 6: Review and Improve
Regularly review your risk management framework to adapt to new threats and industry changes.
Benefits of Proactive Risk Management for MSPs and MSSPs
- Client Trust: Demonstrating a strong risk management strategy builds client confidence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay ahead of regulations and avoid penalties.
- Operational Continuity: Reduce downtime and maintain consistent service delivery.
- Competitive Edge: Differentiate your services by offering secure, risk-aware solutions.
Conclusion
Risk management is a critical component of success for MSPs. By identifying risks, creating a comprehensive framework, and embedding best practices into daily operations, MSPs can safeguard their business and enhance client relationships.
Start strengthening your risk management strategy today to stay resilient in an ever-evolving landscape!
Request Callback