Overview
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a strategic approach that enables businesses to manage their operations while adhering to compliance requirements and minimizing risk. This is particularly crucial for Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs), which handle sensitive data and complex systems for their clients. This guide delves into the components of GRC, its significance, and the substantial benefits it offers to MSSPs.
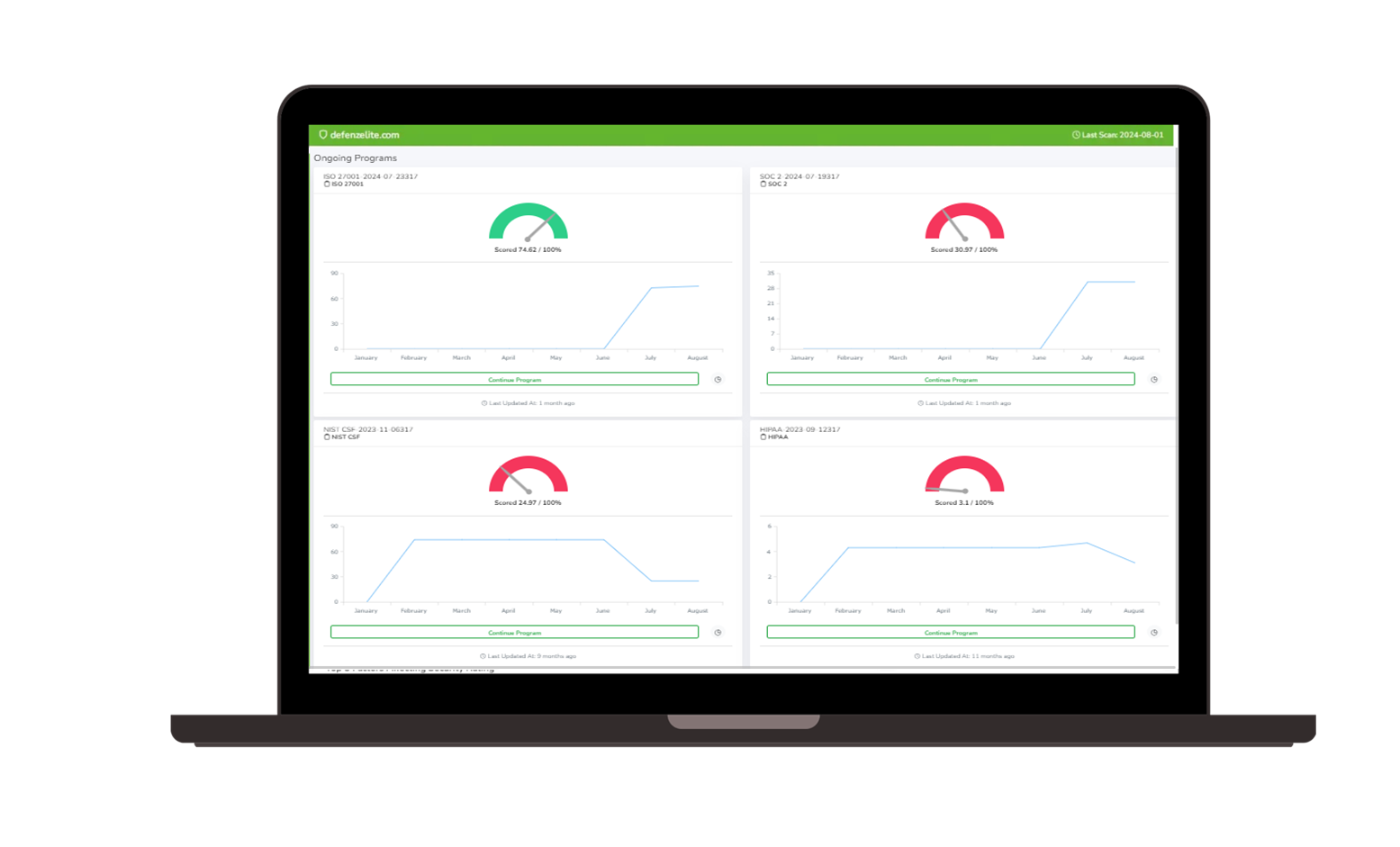 Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) | 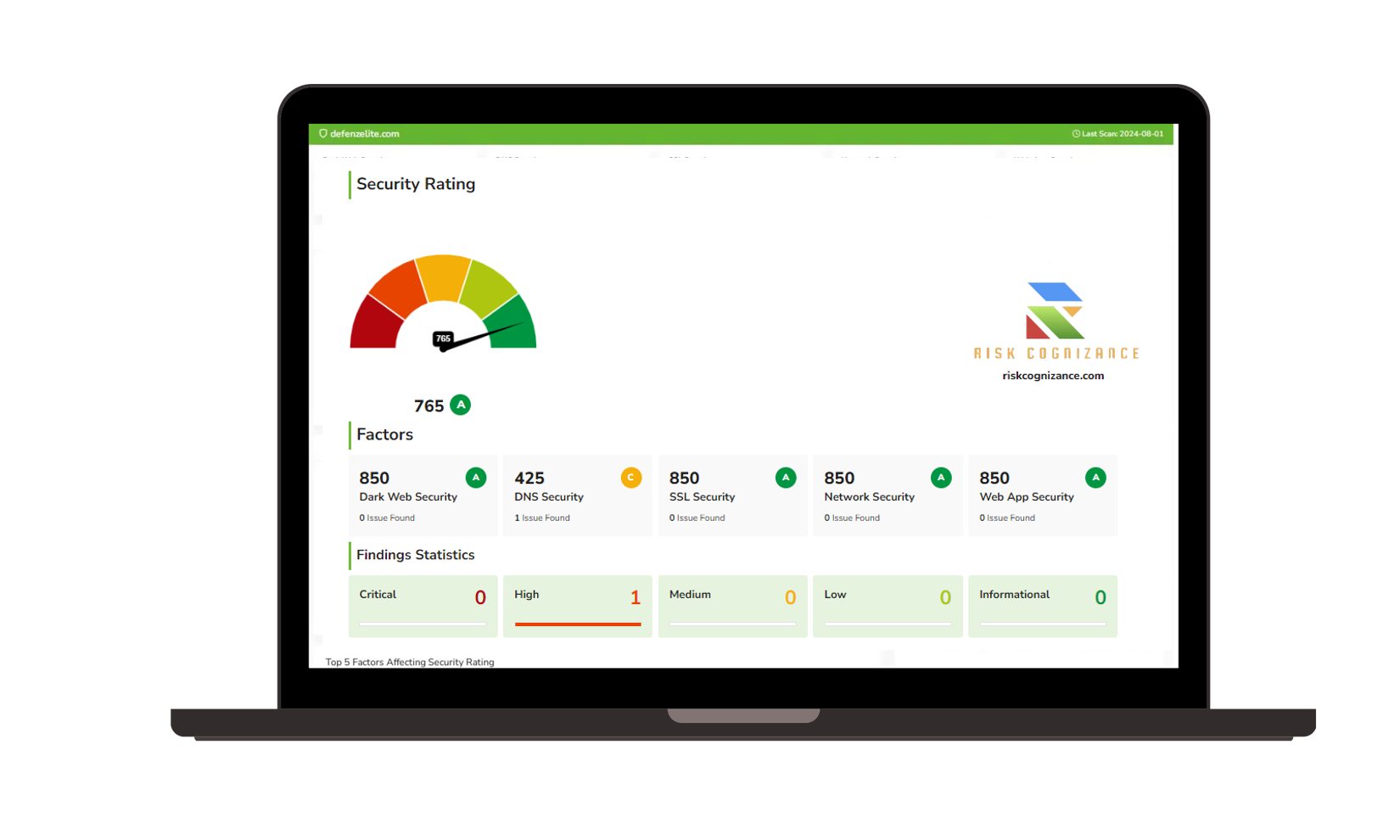 Third-party Risk Management |
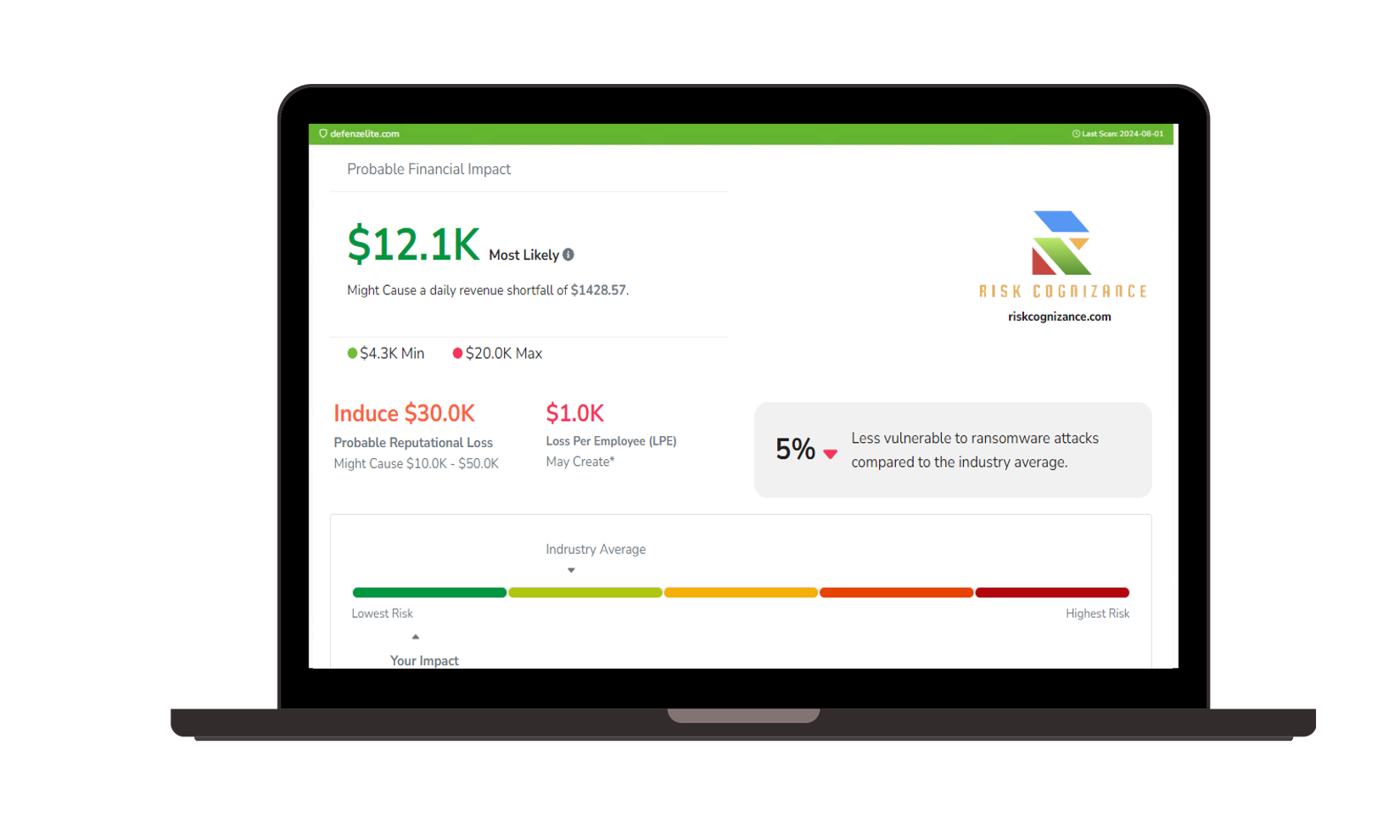 Ransomware Susceptibility | 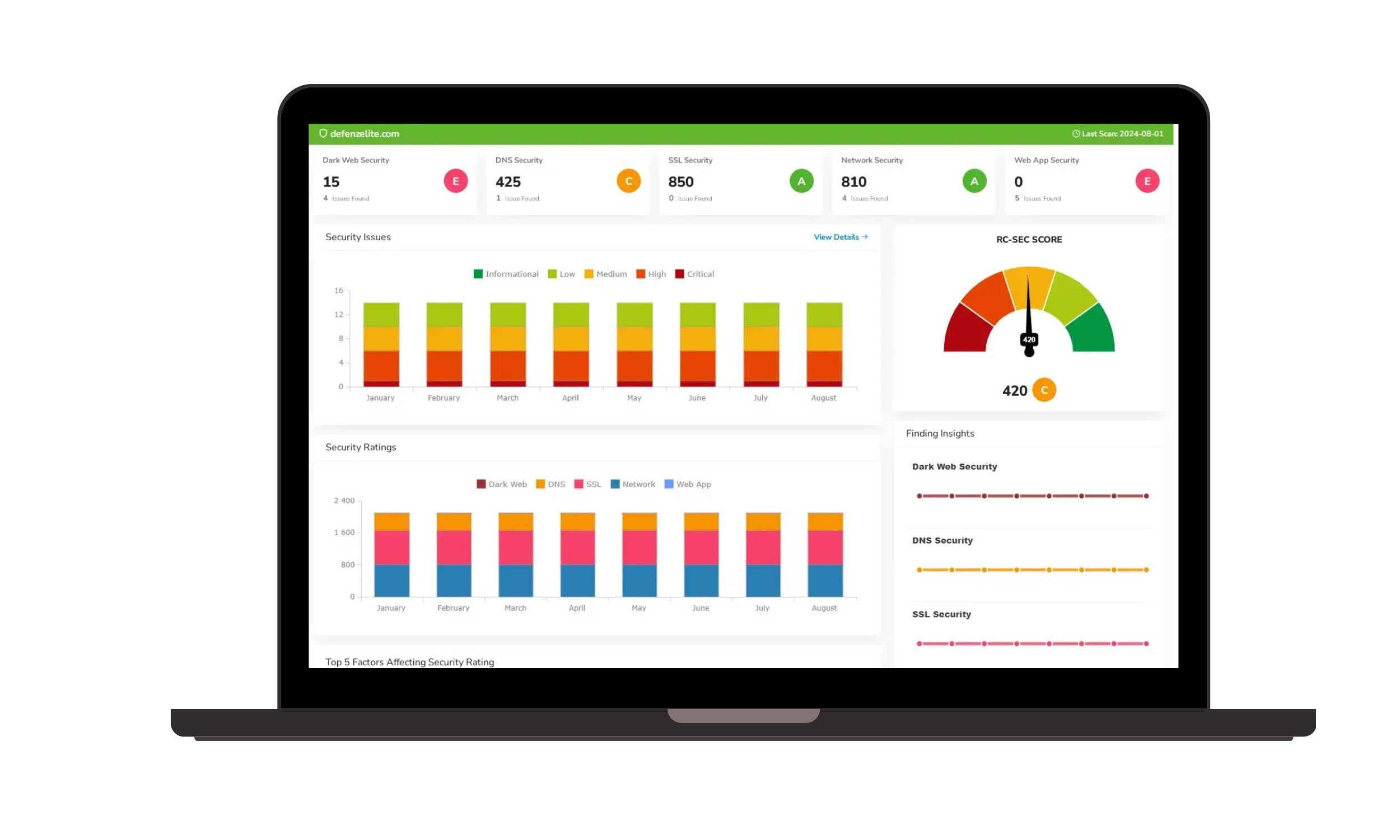 GRC and Attack Surface |
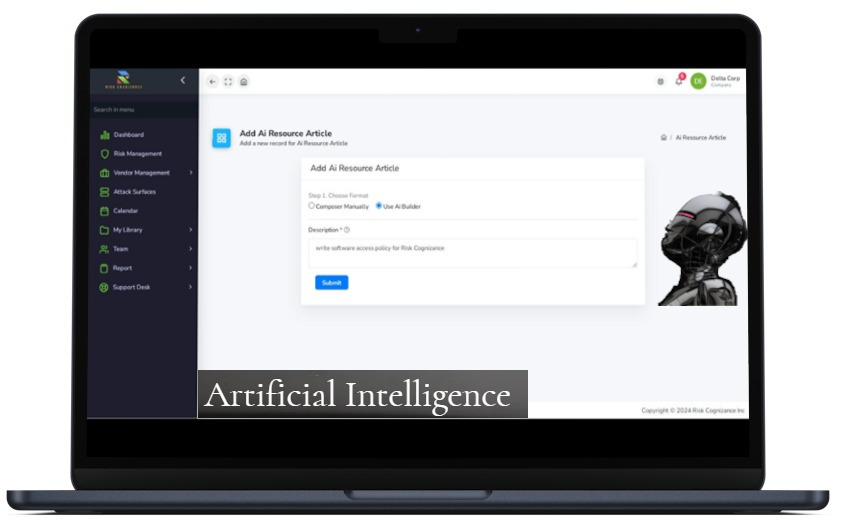
Artificial Intelligence | |
Why is GRC Important for MSSPs?
The importance of GRC for MSSPs cannot be overstated. Here’s why it matters:
- Data Sensitivity: MSSPs manage sensitive client data, making it critical to have strong governance, risk, and compliance measures in place to prevent breaches and data loss.
- Regulatory Pressures: The cybersecurity landscape is filled with regulations and standards that MSSPs must adhere to, including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, which require comprehensive GRC frameworks to ensure compliance.
- Client Trust: Clients need assurance that their data is handled securely and in compliance with regulations. A strong GRC strategy fosters trust and strengthens client relationships.
What is GRC?
GRC consists of three interrelated facets:
Governance:
The practices and processes that ensure an organization is effectively managed, aligning operations with strategic objectives.
Risk Management:
The identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks, followed by actions to mitigate or control them. This proactive approach safeguards MSSPs and their clients.
Compliance:
Ensuring adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies, which is vital for maintaining trust and integrity in client relationships.
Types of Businesses That Benefit from GRC
While GRC is essential for all organizations, the following types particularly benefit:
- MSSPs: Need robust GRC frameworks to manage security risks and ensure compliance for clients.
- Healthcare Organizations: Must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA and manage sensitive patient data.
- Financial Services: Require stringent compliance measures and risk management strategies to protect customer data and adhere to regulations.
- Technology Firms: Need to manage vulnerabilities in software and infrastructure while maintaining compliance with data protection laws.
Internal vs. External GRC Approaches
When implementing a GRC strategy, organizations must decide between internal and external approaches:
Internal GRC:
- Description: Organizations build their GRC capabilities internally, using in-house teams to manage governance, risk, and compliance efforts.
- Benefits:
- Tailored Solutions: Customization to fit specific organizational needs and culture.
- Direct Control: Greater control over processes and policies, ensuring alignment with business objectives.
- Immediate Response: Faster response times to emerging risks and compliance issues.
- Challenges:
- Resource Intensive: Requires significant investment in training, personnel, and technology.
- Scalability Issues: May struggle to scale as the organization grows or faces new regulatory demands.
External GRC:
- Description: Organizations outsource GRC functions to specialized third-party providers (like MSSPs) with expertise in governance, risk management, and compliance.
- Benefits:
- Expertise: Access to specialized knowledge and resources that may not be available internally.
- Cost-Effective: Reduced costs associated with hiring, training, and maintaining a full-time internal GRC team.
- Scalability: Flexibility to scale GRC efforts quickly in response to changing business needs and regulations.
- Challenges:
- Less Control: Potential for misalignment with organizational culture or objectives.
- Dependency Risks: Reliance on external partners for critical governance and compliance functions.
Benefits of GRC for MSSPs
Implementing a robust GRC framework can provide numerous advantages for MSSPs, including:
Enhanced Data Protection:
GRC helps protect sensitive data by establishing robust security policies and practices.
Reduced Downtime:
A well-defined GRC strategy minimizes downtime during unexpected disruptions.
Reduced Legal and Financial Risks:
Maintaining compliance mitigates legal and financial risks associated with noncompliance.
Streamlined Processes:
GRC software can automate compliance processes and provide a centralized view of compliance and cybersecurity data.
Clear Reporting Timelines:
GRC tools establish clear timelines for reporting compliance status to stakeholders.
Compliance Management in GRC
Effective compliance management is a cornerstone of GRC. It involves:
- Policy Development: Establishing clear policies and procedures that govern compliance efforts.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly assessing compliance status through audits and monitoring to ensure adherence to regulations.
- Training and Awareness: Providing training for employees to foster a culture of compliance within the organization.
Attack Surface Management
Attack surface management is crucial for MSSPs to understand and protect their systems. It involves:
- Identifying Assets: Cataloging all digital assets and entry points that could be exploited by attackers.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly assessing the attack surface to identify vulnerabilities and threats.
- Mitigation Strategies: Implementing controls and measures to reduce the potential attack surface and protect client data.
Vulnerability Management and Testing
Vulnerability management and testing are essential components of a GRC framework, including:
- Regular Assessments: Conducting vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses in systems.
- Prioritization and Remediation: Evaluating identified vulnerabilities and implementing remediation plans based on risk severity.
- Continuous Improvement: Establishing a feedback loop to enhance security measures and improve resilience against future threats.
Testimonials
"Implementing Risk Cognizance's GRC platform has transformed how we manage compliance and risk for our clients. The platform’s robust tools streamline our processes, reduce downtime, and enhance data security across the board. As an MSSP, it’s a game-changer!"
— Bancroft Wilson, CEO of Advanced Techco
"Risk Cognizance’s platform has simplified our compliance management and significantly enhanced our ability to protect sensitive data. It’s become a core part of our strategy for safeguarding both our assets and our clients'."
— Liza Davis, Compliance Officer at Mega Mart