Overview
Compliance: Empowering Businesses with Security & Data Protection
Overview
Compliance is a critical component of any business operation, ensuring that organizations adhere to laws, regulations, and industry standards. With security and data protection becoming increasingly important, companies must meet various compliance requirements to safeguard their data and protect against cyber threats. Risk Cognizance offers a comprehensive GRC platform that streamlines the management of security compliance, helping businesses achieve peace of mind while maintaining an efficient and compliant operation.
 Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) | 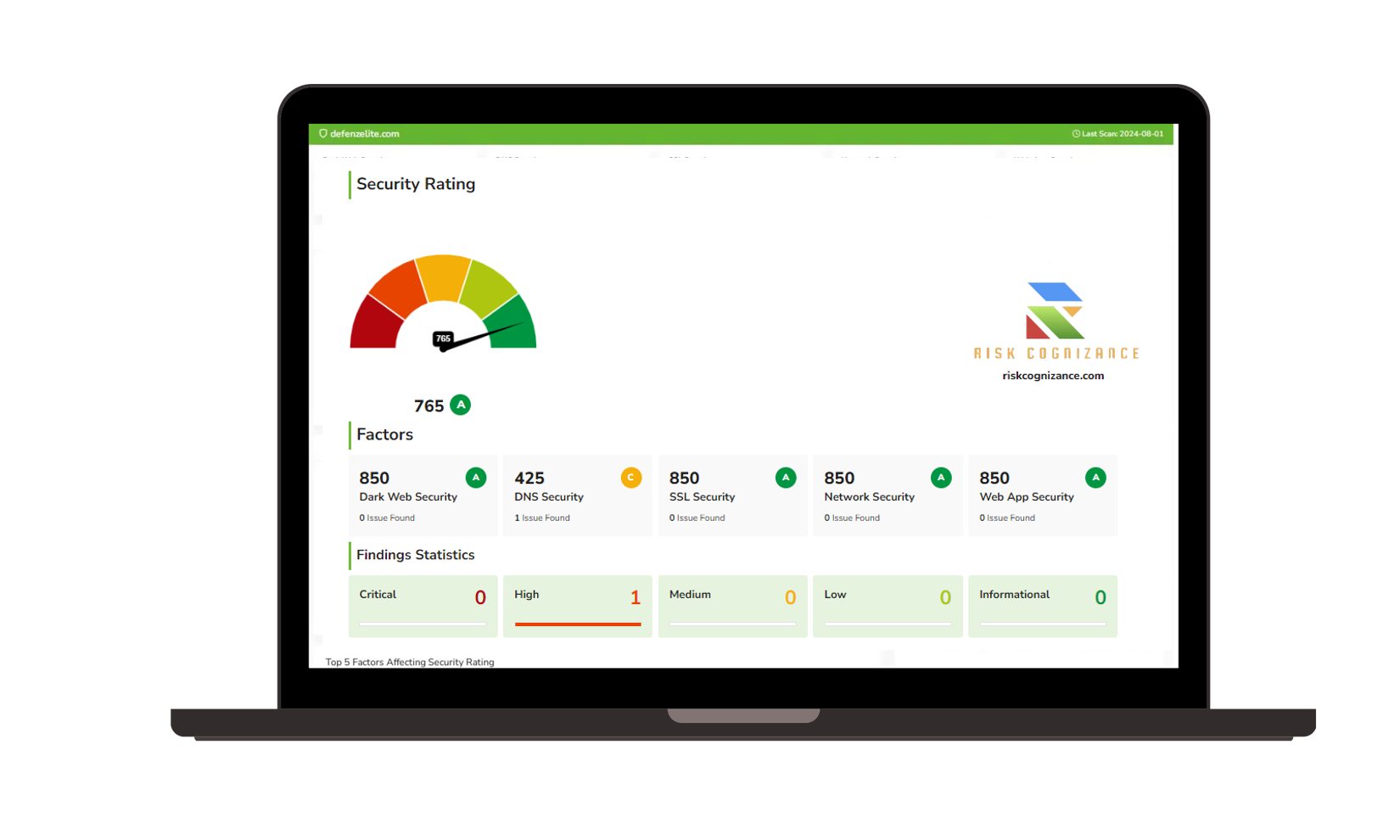 Third-party Risk Management |
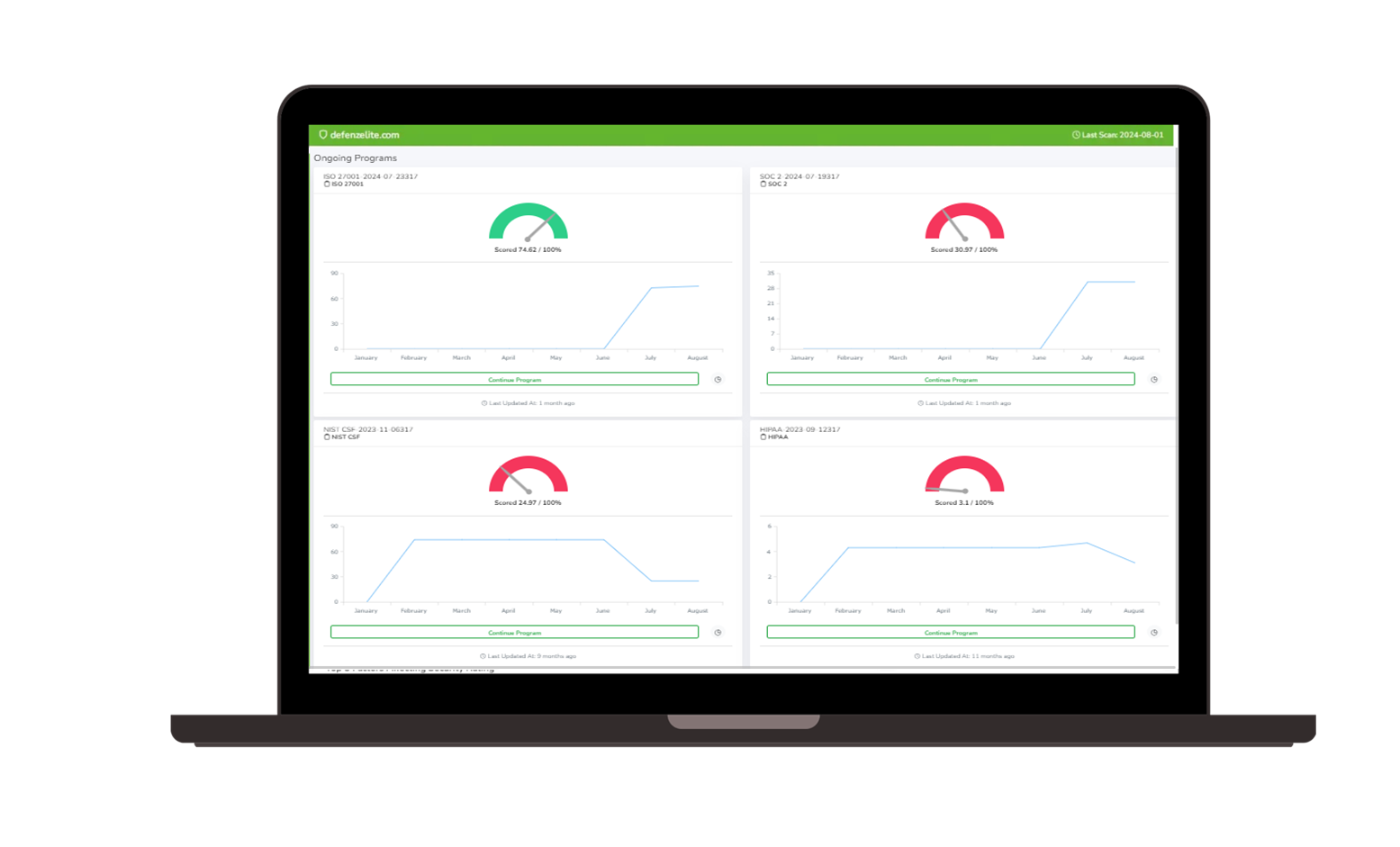
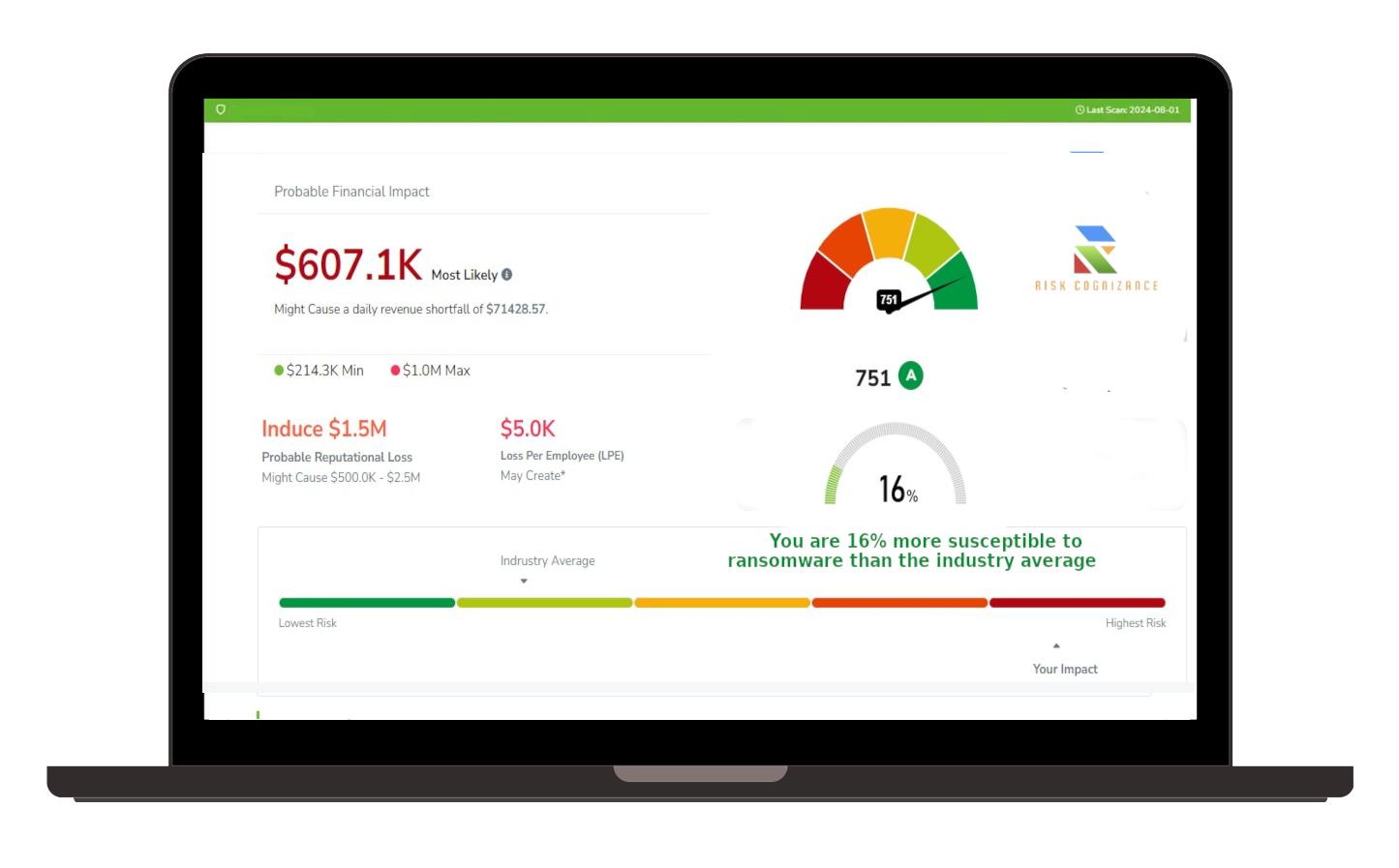 Ransomware Susceptibility | 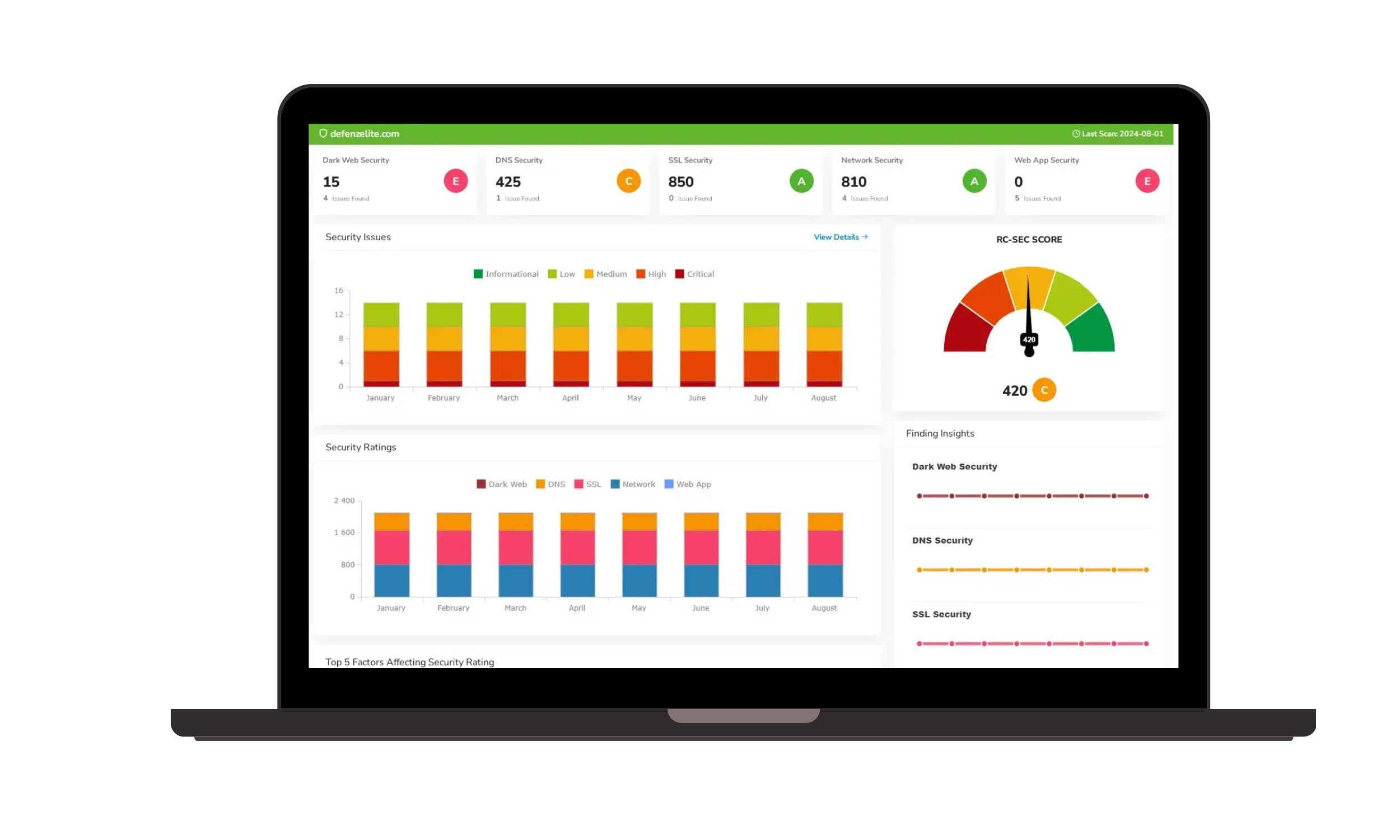 GRC and Attack Surface |
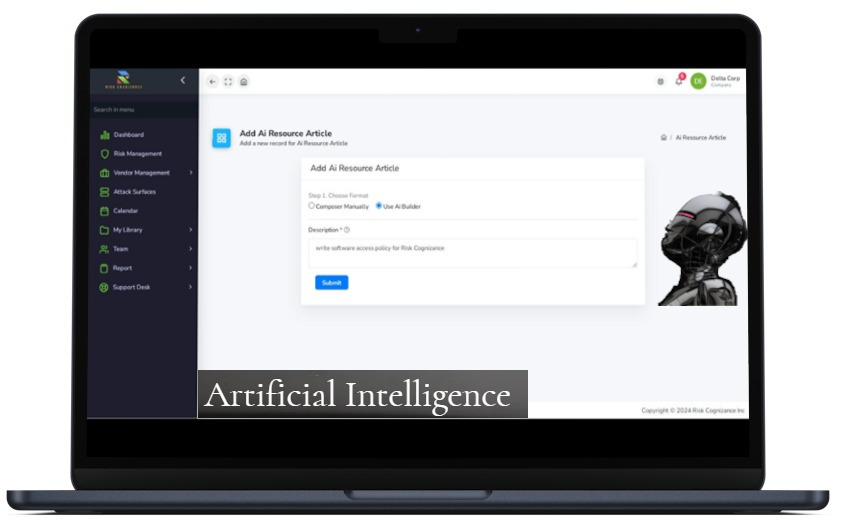
Artificial Intelligence | |
12 Types of Security & Data Protection Compliance
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Governs data protection and privacy within the European Union and for any organization dealing with EU citizens' data.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Ensures the protection of sensitive patient information within healthcare organizations.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Protects cardholder data in businesses that process, store, or transmit credit card information.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP)
Provides a standardized approach to security for cloud services used by the U.S. federal government.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
A cybersecurity framework to protect Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
Regulates how businesses collect, use, and share the personal information of California residents.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
Requires publicly traded companies to establish financial and IT controls to ensure accuracy and transparency in reporting.
ISO/IEC 27001
Provides requirements for an information security management system (ISMS) to protect organizations' sensitive data.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
Enforces financial institutions to protect the confidentiality of customer financial data.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) SP 800-53
Sets guidelines for managing information security risks in federal information systems.
Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA)
Protects the personal information of children under the age of 13 collected by online services.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
Regulates registered brokers and brokerage firms in the U.S., requiring them to protect customer data.
Compliance Definition
Compliance refers to adhering to rules, laws, and regulations imposed by government bodies or industry standards. Compliance ensures that organizations meet ethical, security, and legal obligations, particularly in managing data and cybersecurity practices.
Compliance Meaning
In a business context, compliance involves maintaining policies and practices that follow external regulations and internal guidelines, especially concerning data privacy, security, and financial operations.
Benefits of Compliance and Why a GRC Platform Like Risk Cognizance
Risk Mitigation
Compliance ensures that an organization identifies and addresses risks related to security breaches and data mismanagement.
Regulatory Alignment
Being compliant with regulations ensures that the organization avoids legal penalties and reputational damage.
Improved Security Posture
Implementing compliance frameworks helps businesses establish and maintain strong cybersecurity defenses.
Operational Efficiency
With automated compliance processes, organizations can save time and resources, allowing teams to focus on other critical tasks.
Trust and Reputation
Demonstrating compliance shows customers, partners, and stakeholders that the organization is serious about protecting sensitive information.
Competitive Advantage
Companies that comply with the latest standards gain an edge over competitors by being trusted partners in their industry.
Avoid Fines and Penalties
Non-compliance can lead to significant fines, legal repercussions, and loss of business credibility.
Continuous Improvement
A GRC platform like Risk Cognizance enables organizations to automate compliance, track their progress, and ensure ongoing improvements in security management.
8 Security Compliance Frameworks
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
Provides guidance on how to improve security resilience and reduce cyber risks.
ISO 27001
Sets the global standard for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS).
SOC 2
Addresses how businesses manage data to protect the privacy and confidentiality of their clients.
CIS Critical Security Controls
Offers prioritized cybersecurity actions that organizations can take to protect their data from known cyber threats.
HITRUST CSF
A certifiable framework used by healthcare organizations to comply with industry standards like HIPAA and NIST.
FISMA
Requires federal agencies and contractors to implement and manage data security programs.
CMMC
Ensures that contractors working with the Department of Defense meet basic cybersecurity requirements.
COBIT
A framework for managing IT governance and ensuring that IT investments support an organization's goals.
Why Compliance Should Be Implemented Even if It’s Not Regulated
Even when compliance isn't legally required, adopting compliance frameworks can drastically improve an organization's security posture and operational efficiency. Compliance ensures data is handled responsibly, reducing the risk of cyber threats, data breaches, and system disruptions. It builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, positioning the company as a leader in ethical business practices. Additionally, regulatory compliance often becomes mandatory over time, and early adoption prepares organizations for future requirements.
Risk Cognizance GRC Platform Software Features
Automated Risk Assessments
Quickly assess risks and generate reports using automated tools for better decision-making.
Compliance Tracking
Monitor multiple compliance frameworks, ensuring your organization stays ahead of regulatory requirements.
Real-Time Risk Scoring
Gain insights into your security controls' effectiveness through real-time risk scores and analysis.
AI-Powered Documentation
Use generative AI to create policies, reports, and compliance documentation with increased accuracy and speed.
Vendor Risk Management
Track and manage risks from third-party vendors, ensuring all partners comply with your security standards.
Case & Incident Management
Handle security incidents and manage cases through an integrated system that ensures swift responses.
Attack Surface Management
Identify vulnerabilities and reduce your attack surface with tools designed to strengthen your defenses.
Audit Management
Streamline audits with automated workflows, ensuring your organization is audit-ready at all times.
Emphasizes the importance of compliance, highlights key security frameworks, and presents the comprehensive features of the Risk Cognizance GRC platform, positioning it as the ideal solution for businesses looking to enhance their compliance and security practices.
Request Callback