What is HIPAA?
In the realm of healthcare, protecting patient information is of utmost importance. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a pivotal piece of legislation that sets the standard for safeguarding sensitive patient data. Let's explore what HIPAA is, its key provisions, and its impact on healthcare providers and patients.
Understanding HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1996. Its primary objectives are to improve the portability and continuity of health insurance coverage, reduce healthcare fraud and abuse, mandate industry-wide standards for healthcare information on electronic billing and other processes, and ensure the protection and confidential handling of protected health information (PHI).
Key Provisions of HIPAA
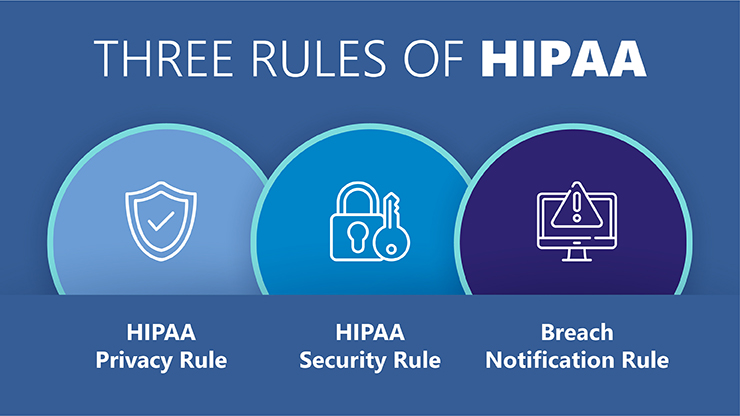
HIPAA comprises several rules that establish standards for protecting health information. The most notable ones include:
Privacy Rule: The Privacy Rule establishes national standards for the protection of individually identifiable health information. It governs how healthcare providers, health plans, and their business associates can use and disclose PHI.
Security Rule: The Security Rule specifies a series of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards that covered entities must implement to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Breach Notification Rule: This rule requires covered entities to notify affected individuals, the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media of a breach of unsecured PHI. Business associates must notify covered entities if a breach occurs at or by the business associate.
Enforcement Rule: The Enforcement Rule outlines provisions relating to compliance and investigations, including the imposition of civil money penalties for violations of HIPAA.
Omnibus Rule: Introduced in 2013, the Omnibus Rule strengthens HIPAA's privacy and security protections and expands the requirements for business associates.
Who Does HIPAA Apply To?
HIPAA applies to two main groups:
Covered Entities: These include healthcare providers (e.g., doctors, clinics, hospitals), health plans (e.g., health insurance companies, HMOs), and healthcare clearinghouses that process nonstandard health information into a standard format.
Business Associates: These are entities that perform functions or activities on behalf of, or provide certain services to, a covered entity that involve the use or disclosure of PHI. Examples include billing companies, law firms, and IT service providers.
Impact on Healthcare Providers
HIPAA has a profound impact on healthcare providers and their operations:
Compliance Requirements: Healthcare providers must implement policies and procedures to comply with HIPAA's privacy and security rules. This includes conducting risk assessments, training staff, and establishing safeguards for PHI.
Patient Rights: HIPAA grants patients several rights regarding their health information, including the right to access their records, request corrections, and obtain a record of disclosures.
Data Security: Providers must ensure the security of electronic health information through encryption, access controls, and regular audits to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Benefits for Patients
HIPAA provides numerous benefits for patients, including:
Privacy and Security: Patients' health information is protected from unauthorized access, ensuring their privacy and confidentiality.
Access to Information: Patients have the right to access their health records, empowering them to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Control Over Information: Patients can request corrections to their health information and have a say in how their information is used and disclosed.
Conclusion
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a cornerstone of patient data protection in the healthcare industry. By establishing stringent standards for the privacy and security of health information, HIPAA ensures that patients' sensitive data is safeguarded while granting them greater control over their information. For healthcare providers, compliance with HIPAA is essential to maintaining trust and delivering quality care. Understanding and adhering to HIPAA's provisions is crucial in today's digital age, where the protection of personal information is more important than ever.