GRC Software: A Deep Dive into Effective Risk Management and Compliance
Understanding GRC
Before we delve deeper into GRC software, let's clarify what GRC stands for: Governance, Risk, and Compliance. It's a framework that helps organizations manage their risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and maintain effective governance.
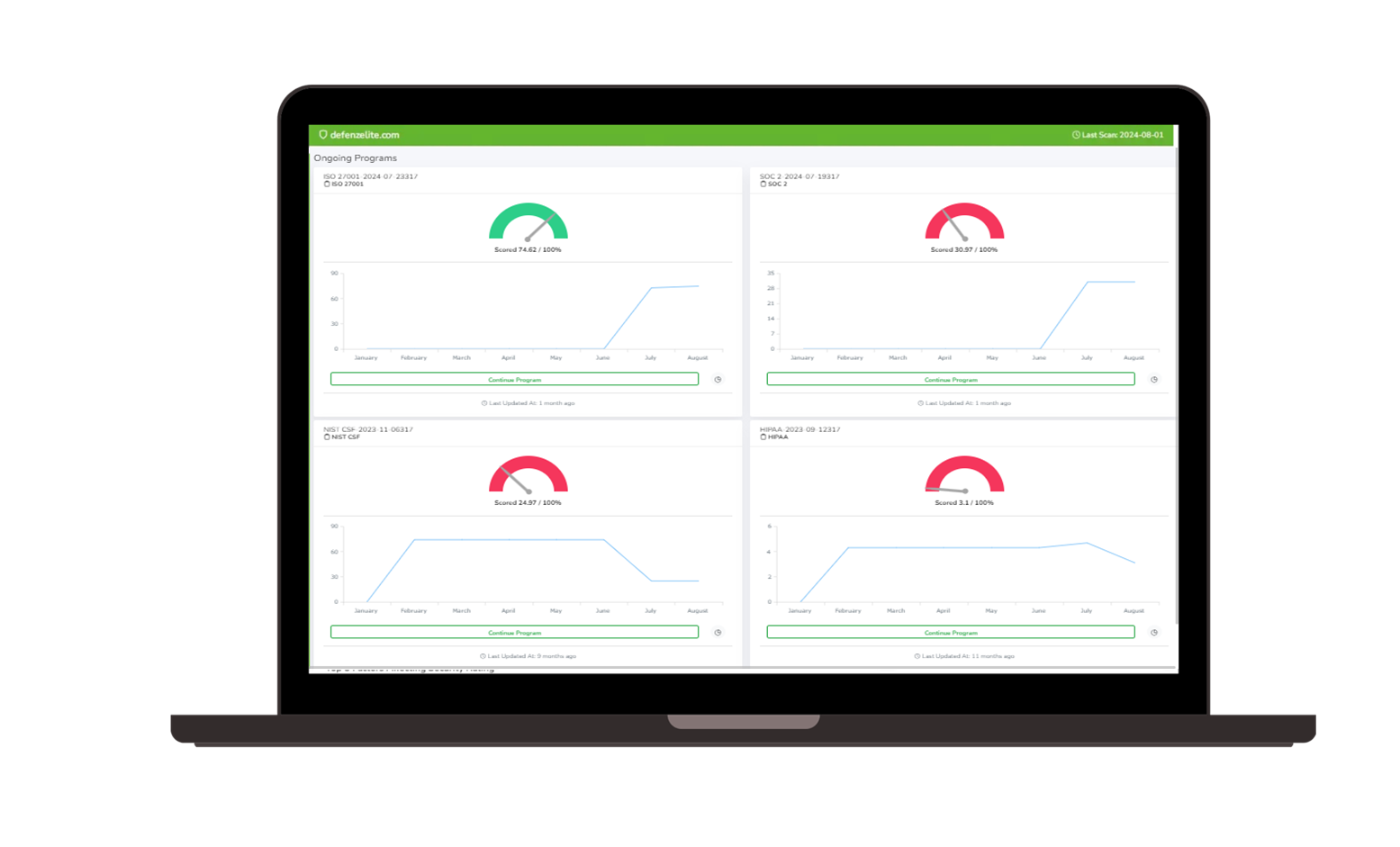 Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) | 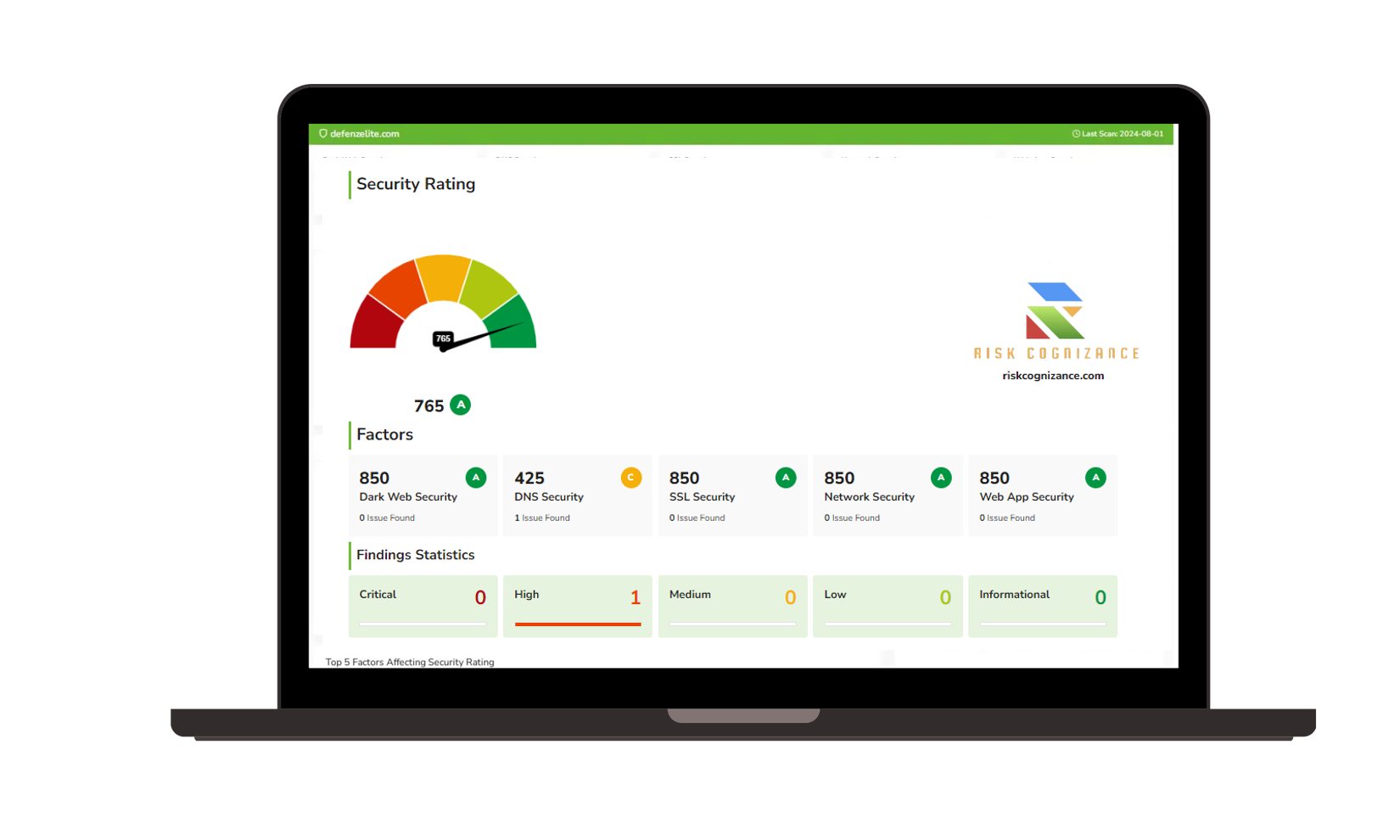 Third-party Risk Management |
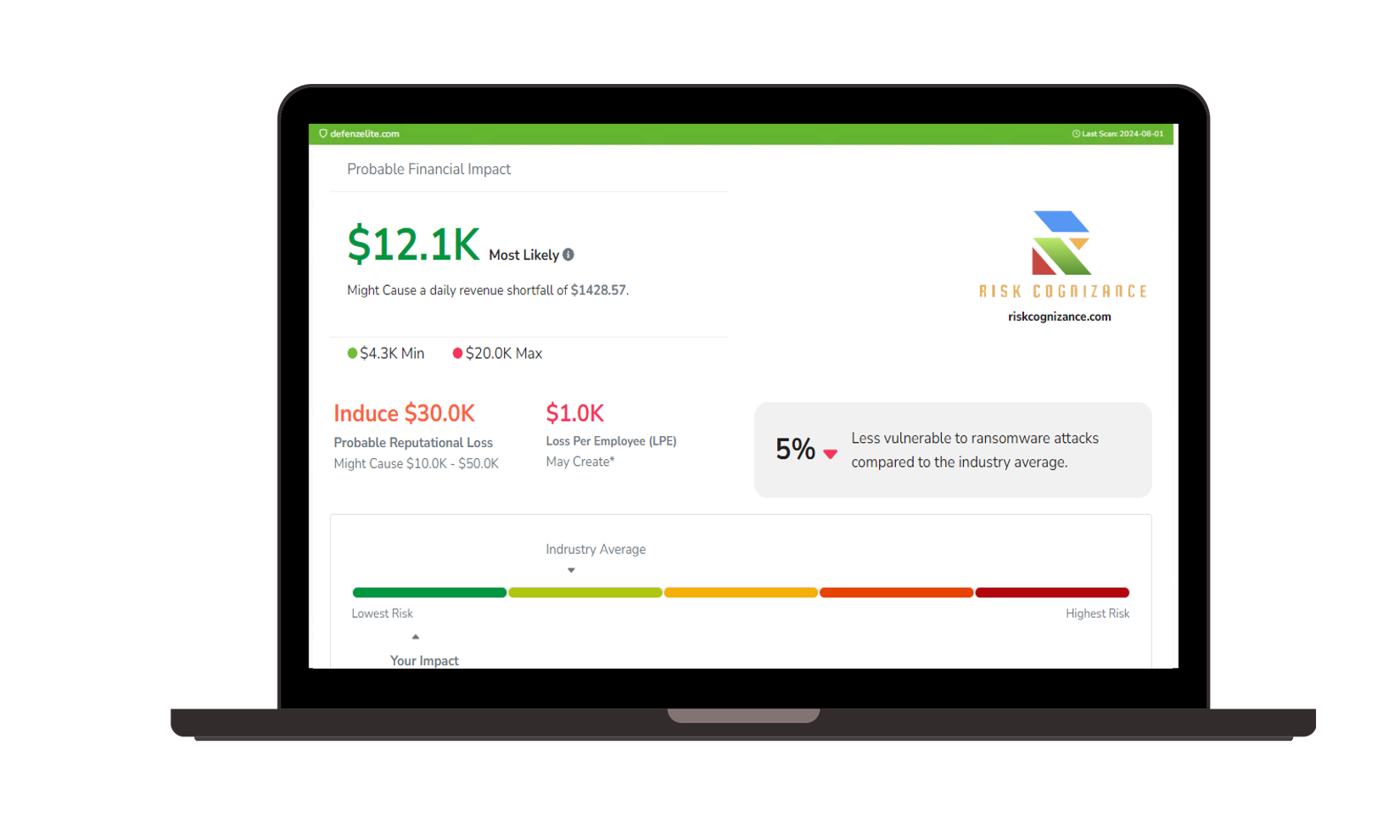 Ransomware Susceptibility | 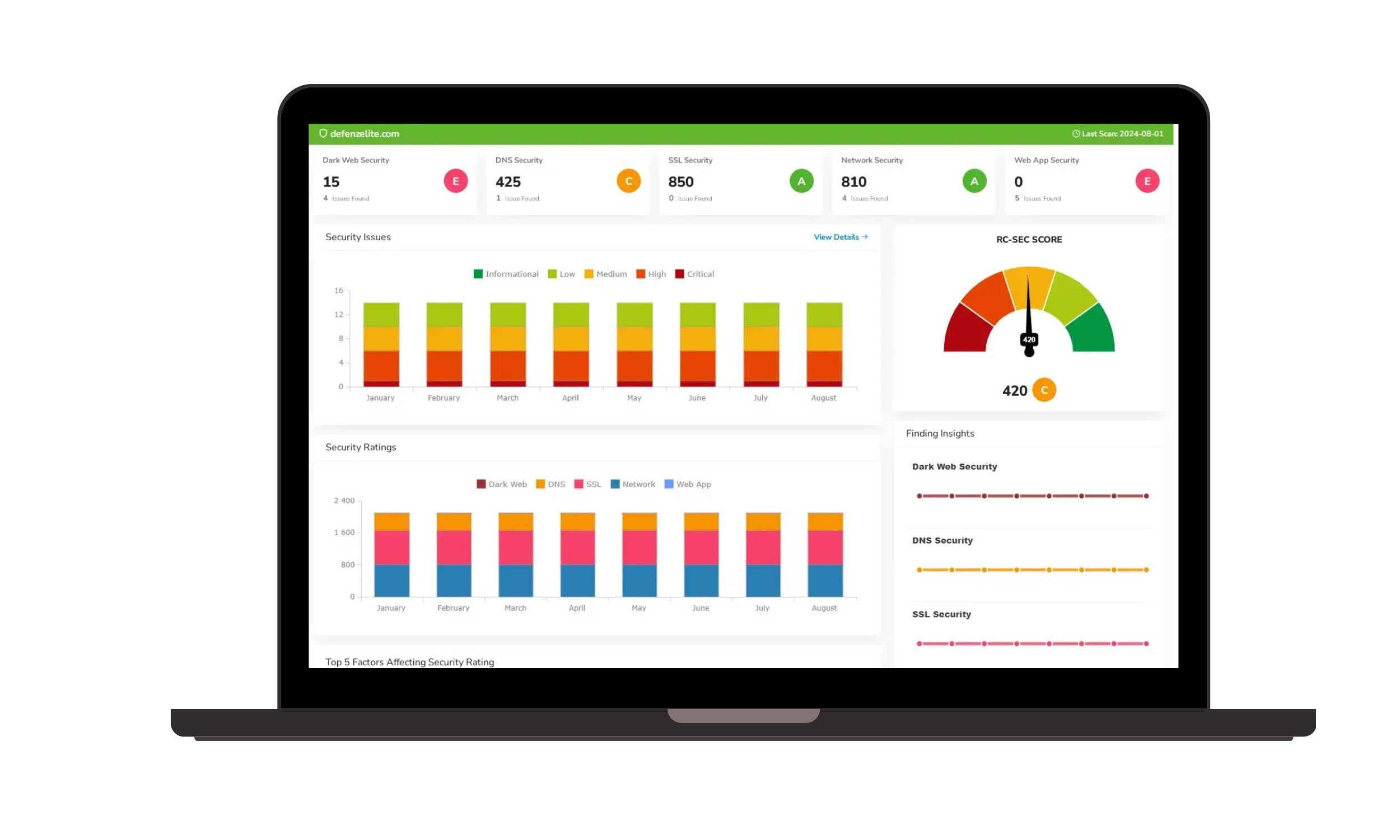 GRC and Attack Surface |
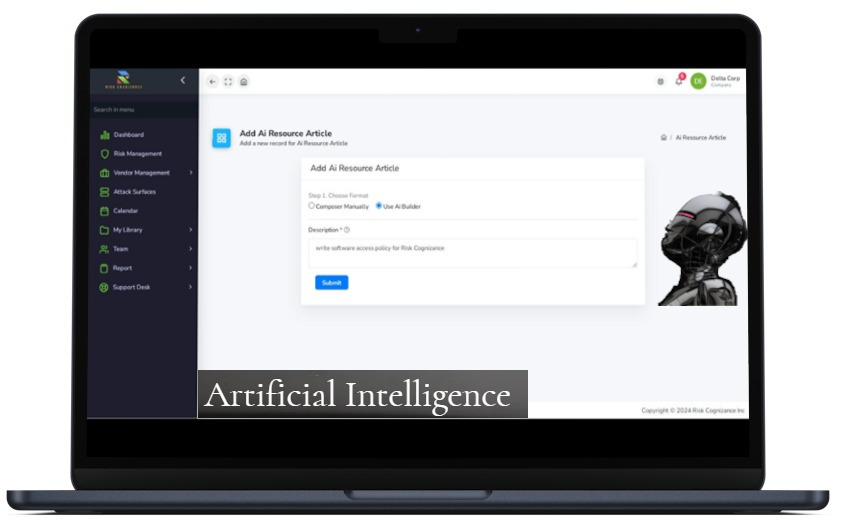
Artificial Intelligence | |
Key Components of a GRC Software
A robust GRC software typically includes the following components:
Risk Management:
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, such as data breaches, cyberattacks, regulatory violations, and operational failures.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks to determine their priority.
- Risk Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their potential consequences and the likelihood of occurrence.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate risks, such as implementing security controls, developing contingency plans, and improving employee training.
Compliance Management:
- Regulatory Tracking: Monitoring changes in relevant regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
- Policy and Procedure Management: Creating, managing, and distributing policies and procedures to ensure compliance with regulations and internal standards.
- Compliance Assessments: Conducting regular assessments to identify gaps and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Audit Management: Planning, conducting, and managing audits to verify compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Governance:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that GRC initiatives align with the organization's overall strategy and objectives.
- Board and Executive Oversight: Providing visibility into GRC activities to senior leadership and ensuring accountability.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving relevant stakeholders, such as employees, customers, and regulators, in the GRC process.
Benefits of Implementing a GRC Software
- Reduced Risk Exposure: Proactively identify and mitigate potential threats to your business, minimizing financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- Enhanced Compliance: Streamline compliance efforts, reduce audit costs, and avoid costly fines and penalties.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Automate manual tasks, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage analytics to gain insights into your organization's risk profile and identify areas for improvement.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Confidence: Demonstrate your commitment to good governance, risk management, and compliance, building trust with customers, investors, and regulators.
Choosing the Right GRC Software
When selecting a GRC software, consider the following factors:
- Scalability: Ensure the software can accommodate your organization's growth and changing needs.
- Customization: The ability to tailor the software to your specific requirements and industry regulations.
- Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with your existing systems and tools to streamline workflows.
- User-Friendliness: An intuitive interface that is easy for employees to use, even without extensive technical knowledge.
- Support and Maintenance: Quality of customer support and maintenance services.
Best Practices for GRC Software Implementation
- Define Your Goals: Clearly articulate your organization's GRC objectives and align them with your overall business strategy.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Ensure buy-in from all relevant departments and individuals to facilitate adoption and success.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Assess your current GRC practices and identify areas for improvement to prioritize your implementation efforts.
- Implement a Phased Approach: Gradually introduce the GRC software to minimize disruption and allow for effective training and adoption.
- Provide Training: Educate employees on how to use the software effectively and understand its benefits.
- Continuously Evaluate and Improve: Regularly review your GRC processes and make necessary adjustments to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Conclusion
By implementing a GRC software and following these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance their risk management, compliance efforts, and overall business performance. A well-chosen GRC software can provide a valuable tool for navigating the complex regulatory landscape and ensuring organizational success.